| USAF Plans To Expand Nuclear Bomber Bases
美国空军计划扩大核轰炸机基地 Date:2020-11-26 Source:FAS By:Globalmil Viewed: |
Posted on Nov.17, 2020 in Arms Control, B-2, B-21, B-52, bombers, Nuclear Weapons, Russia, United States
By Hans M. Kristensen
发表于2020年11月17日,军备控制,B-2,B-21,B-52,轰炸机,核武器,俄罗斯,美国
汉斯·克里斯滕森(Hans M.Kristensen)
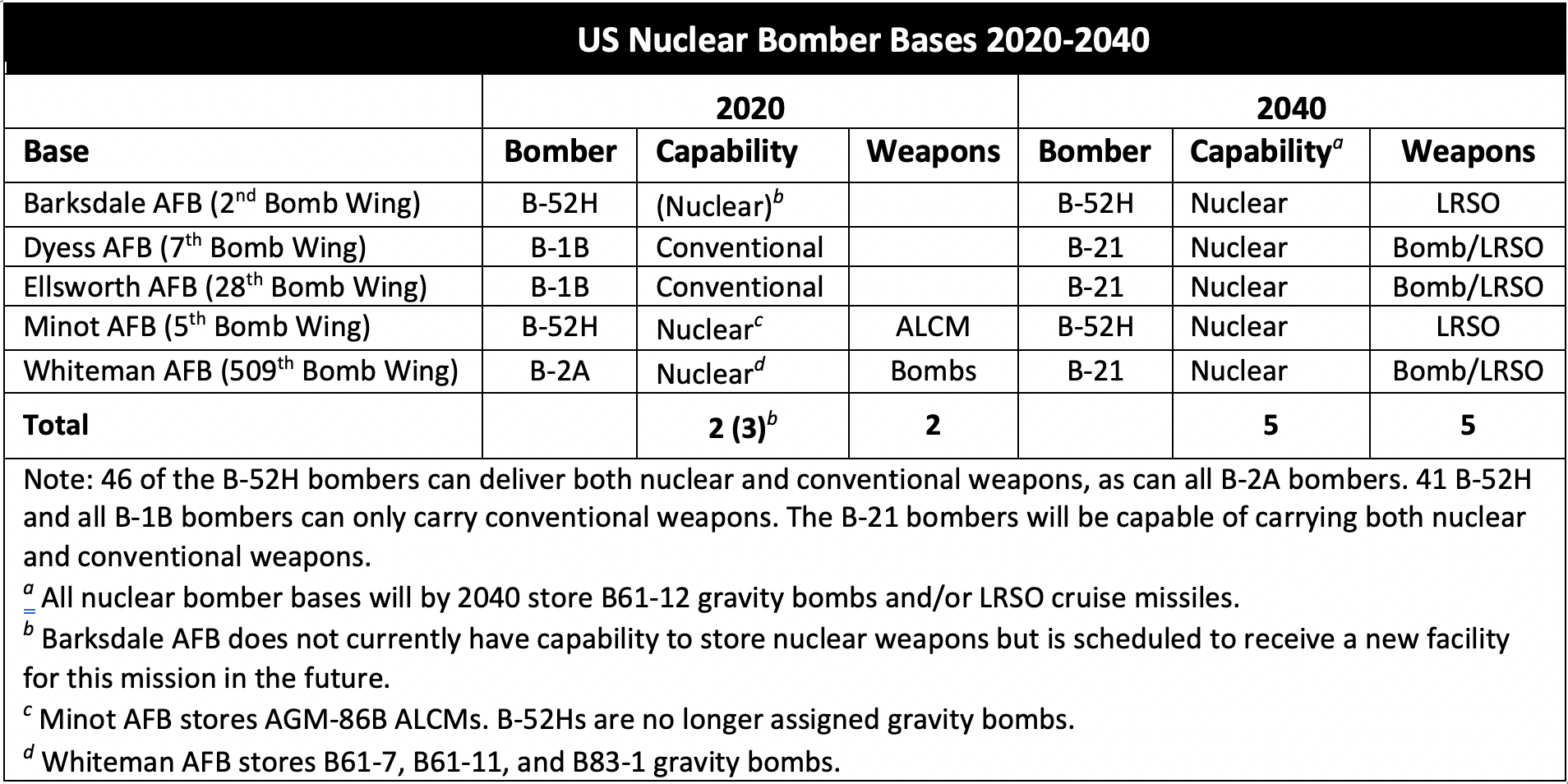
The US Air Force is working to expand the number of strategic bomber bases that can store nuclear weapons from two today to five by the 2030s.
美国空军正在努力将可以储存核武器的战略轰炸机基地的数量从今天的两个增加到2030年的五个。
The plan will also significantly expand the number of bomber bases that store nuclear cruise missiles from one base today to all five bombers bases by the 2030s.
该计划还将显着地将存储核巡航导弹的轰炸机基地的数量从今天的一个基地扩大到2030年代的所有五个轰炸机基地。
The expansion is the result of a decision to replace the non-nuclear B-1B bombers at Ellsworth AFB and Dyess AFB with the nuclear B-21 over the next decade-and-a-half and to reinstate nuclear weapons storage capability at Barksdale AFB as well.
这次扩建是一项决定的结果,即在未来15年内,埃尔斯沃斯空军基地(Ellsworth AFB )和戴斯空军基地(Dyess AFB)将非核B-1B轰炸机替换为核B-21,并恢复巴克斯代尔空军基地(Barksdale AFB)的核武器储存能力。
The expansion is not expected to increase the total number of nuclear weapons assigned to the bomber force, but to broaden the infrastructure to “accommodate mission growth,” Air Force Global Strike Command Commander General Timothy Ray told Congress last year.
美国空军全球打击司令部司令提莫西·雷(Timothy Ray)将军去年向国会表示,这种扩张预计不会增加分配给轰炸机部队的核武器的总数,但会扩大基础设施以“适应任务的增长”。
Nuclear Bomber Base Expansion
核轰炸机基地扩建
The Air Force announced in May 2018 that the B-21 would replace the B-1B and B-2A bombers and be deployed at Ellsworth AFB, Dyess AFB, and Whiteman AFB. The commander of the strategic bomber force later explained in a video address to the B-1B bases that “the B-21 will bring significant changes to each location, to include the reintroduction of nuclear mission requirements.”
美国空军于2018年5月宣布,B-21将取代B-1B和B-2A轰炸机,并部署在埃尔斯沃思空军基地,戴斯空军基地和怀特曼空军基地。战略轰炸机部队的指挥官随后在B-1B基地的视频讲话中解释说:“B-21将会对每个地点带来重大变化,包括重新引入核任务要求。”
Since the B-1B was replaced in the nuclear war plan by the B-2A in 1997 and all B-1B bombers were denuclearized in 2011, the effect of the B-21 bomber program is that nuclear bomber operations will increase from the three bases today to five bases in the future (see map):
由于1997年在核战争计划中B-2A取代了B-1B,而2011年所有B-1B轰炸机都实现无核化,因此B-21轰炸机计划的效果是核轰炸机的行动将从现有三个基地增加到将来的五个基地(参见地图):
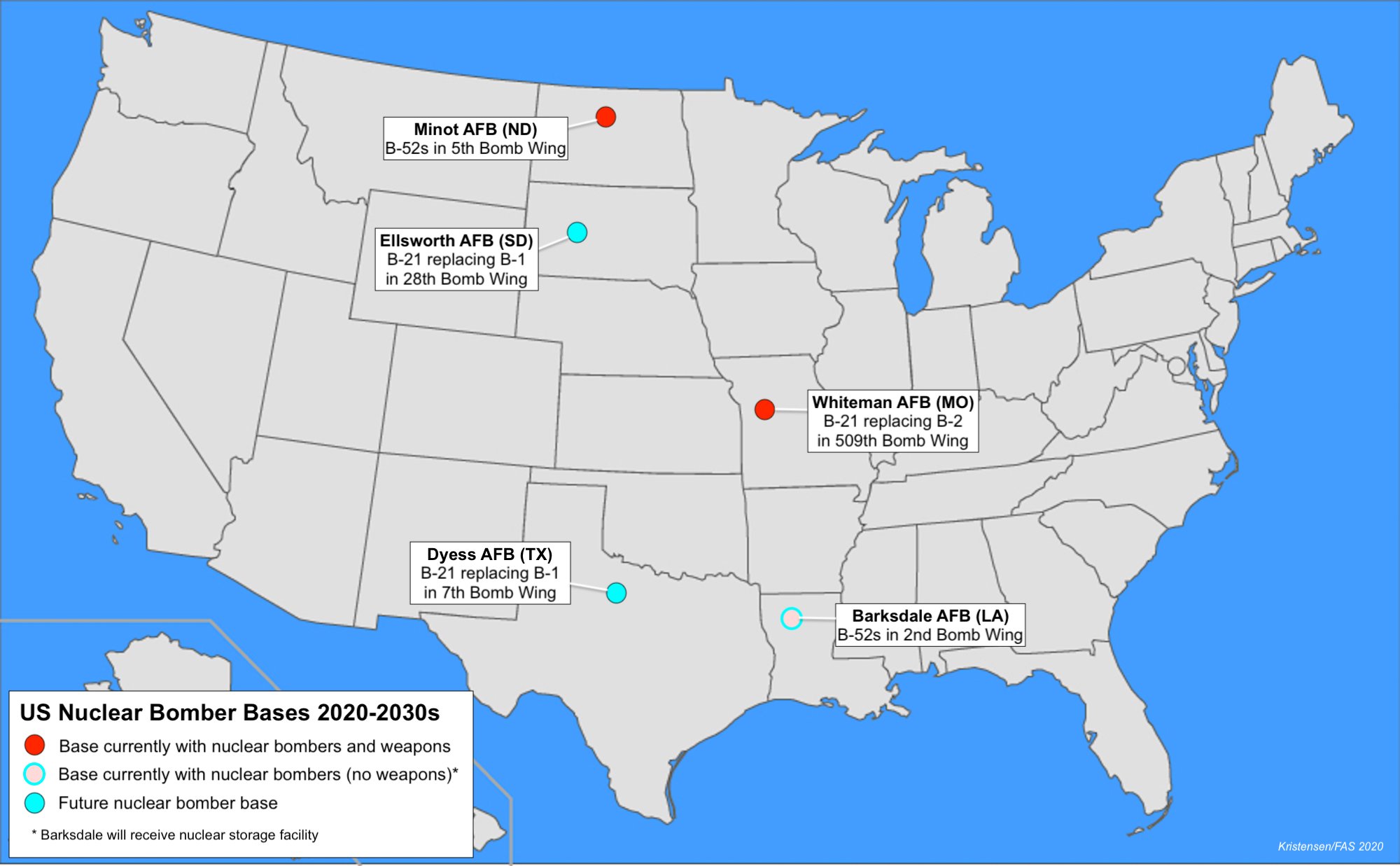
The Air Force plans to increase nuclear weapons storage capacity at bomber bases from two locations today to five in the future.
美国空军计划将轰炸机基地的核武器储存能力从今天的两个地点增加到将来的五个地点。
The Air Force previously planned for the B-21 to replace the B-2A no later than 2032 and the B-1Bs no later than 2036, though those dates may have shifted some since.
空军原先计划在2032年之前用B-21取代B-2A,在2036年之前取代B-1B,不过这些日期可能会有所改变。
The effect of the integration of the B-21 is that bases with nuclear stealth bombers will increase from one today (Whiteman AFB) to three in the future.
B-21一体化的结果是,带有核隐身轰炸机的基地将从今天的一个(怀特曼空军基地)增加到将来的三个。
The modernization plan also appears to significantly expand the location of nuclear cruise missiles from one base today (Minot AFB) to all five bomber bases by the late-2030s. The LRSO is scheduled to begin entering the arsenal in 2030 (see table):
现代化计划似乎也将在2030年后期将核巡航导弹的地点从今天的一个基地(迈诺特空军基地,Minot AFB)大大扩展到所有五个轰炸机基地。 远程制导武器(LRSO)计划于2030年开始进入军火库(见表):
美国空军计划大幅扩展核轰炸机基地及其能力。
Nuclear Storage Facilities
核储存设施
A key element of the base upgrades to operate the B-21 involves the construction of a new nuclear weapons storage facility at each base: a Weapons Generation Facility (WGF). The new facility is different than the Weapons Storage Areas (WSAs) that that the Air Force built during the Cold War because it will integrate maintenance and storage mission sets into the same facility. The WGF will have a footprint of roughly 35 acres and include an approximately 52,000-square-foot (4,860 square meters) building as well as a 17,600 square-foot munitions maintenance building. The Air Force says the WGF will be “unique to the B-21 mission” and designed to provide a “safer and more secure location for the storage of Air Force nuclear munitions.”
B-21基地升级的关键要素是在每个基地建设一个新的核武器储存设施:一个武器生产设施(WGF)。新设施不同于空军在冷战期间建造的武器存储区(WSA),因为它将把维护和存储任务集整合到同一设施中。武器生产设施(WGF)的占地面积约为35英亩,包括一座约52,000平方英尺(4,860平方米)的建筑以及一栋17,600平方英尺的弹药维护建筑。美国空军表示,武器生产设施(WGF)将“对于B-21任务而言是独一无二的”,旨在为“储存空军核弹药提供一个更安全和更牢固的地点”。
An WGF is also under construction at F.E. Warren AFB for storage of ICBM warheads.
沃伦空军基地也正在建造一个武器生产设施(WGF),用于储存洲际弹道导弹(ICBM)弹头。
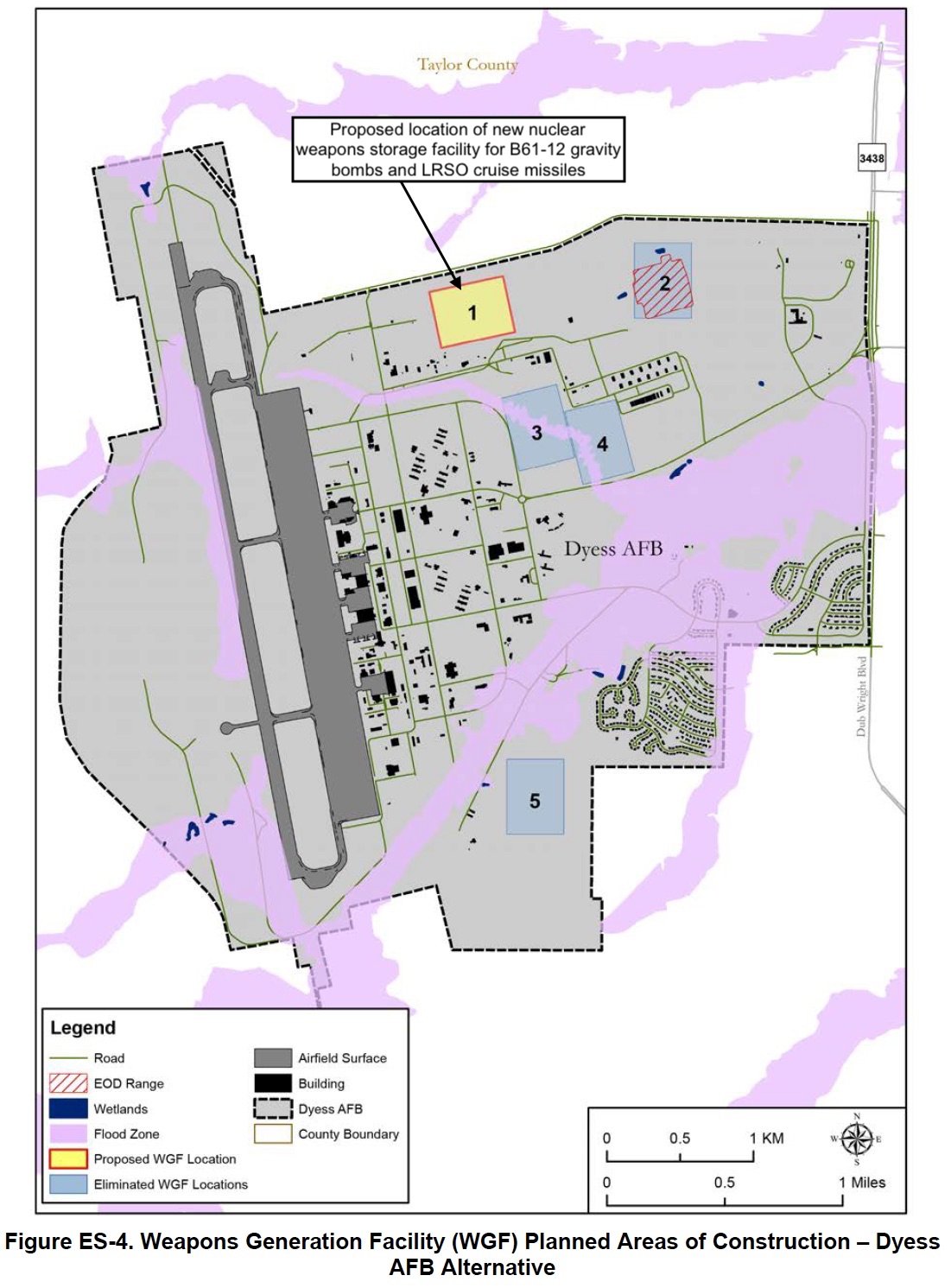
A draft Environmental Impact Statement recently posted by the Air Force shows the planned location of the nuclear weapons storage facility at Dyess and Ellsworth air force bases. At Dyess AFB, the intension is to build facility at the northern end of the base near the current munitions depot (see map below):
美国空军最近发布的一份环境影响报告草案显示了戴斯和埃尔斯沃斯空军基地的核武器储存设施的计划位置。在戴斯空军基地,其目的是在基地北端靠近现有弹药库的地方建造设施(见下图):
The Air Force plans to add nuclear weapons storage capacity to Dyess Air Force Base in Texas.
美国空军计划在德克萨斯州的戴斯空军基地增加核武器储存能力。
At Ellsworth AFB, the Air Force has identified two preferred locations: one at the northern end near the munitions depot, and one at the southern end near the aircraft alert apron (see map below):
在埃尔斯沃思空军基地,空军已经确定了两个首选地点:一个在军火库附近的北端,另一个在飞机警戒停机坪附近的南端(见下图):
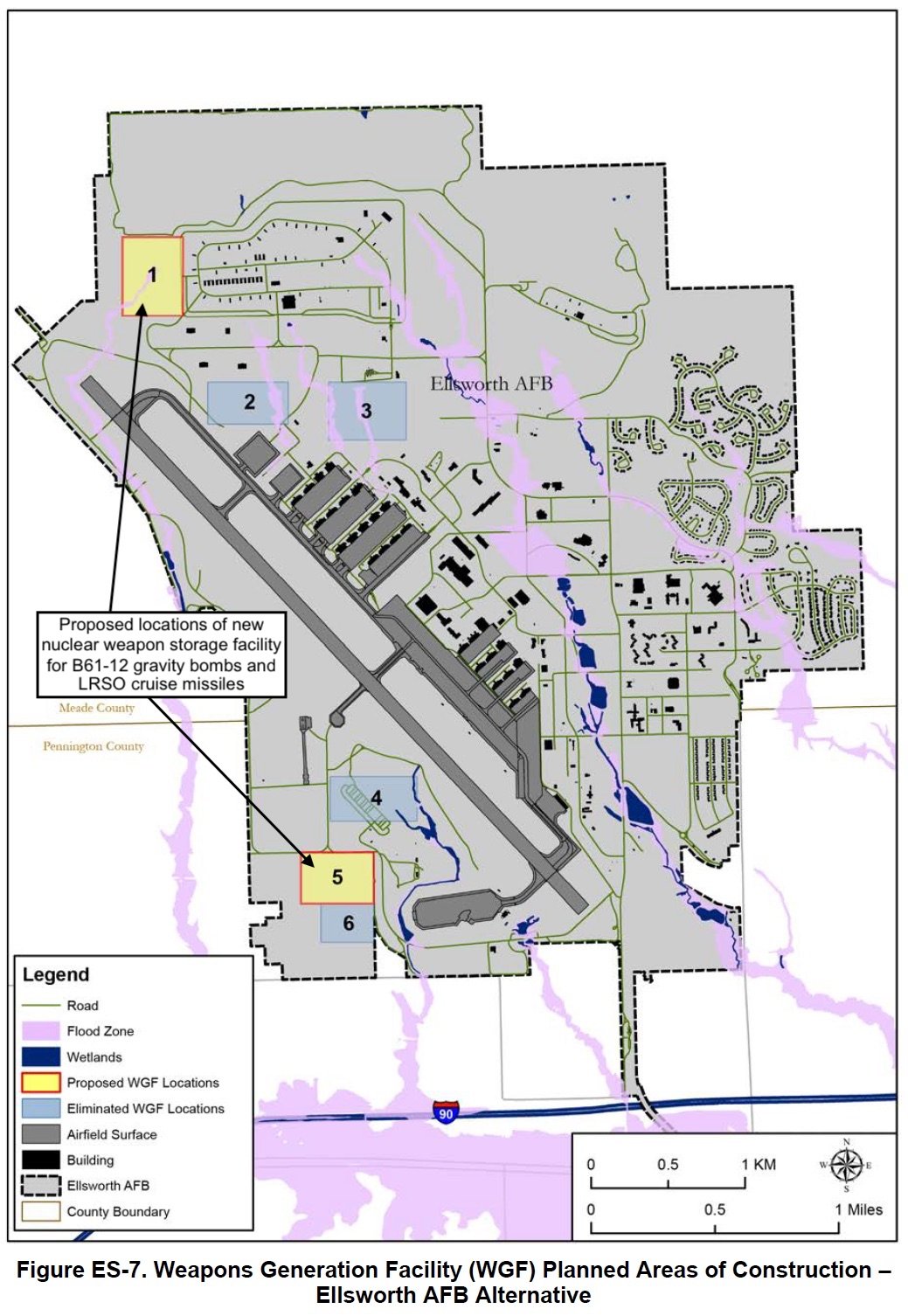
The Air Force plans to add nuclear weapons storage capacity to Ellsworth Air Force Base in South Dakota.
美国空军计划增加南达科他州埃尔斯沃思空军基地的核武器储存能力。
Although Barksdale AFB is not scheduled to receive the B-21, preparations are underway to reinstate the capability to store nuclear weapons at the base. The capability was lost when the Air Force last decade consolidated operational nuclear ALCM storage at Minot AFB. Once completed, the new WGF will enable the base to store nuclear LRSO cruise missiles for delivery by the B-52s.
尽管巴克斯代尔空军基地未计划接收B-21,但仍在准备恢复在基地储存核武器的能力。美国空军过去十年在迈诺特空军基地(Minot AFB)合并了作战核空中发射巡航导弹(ALCM)储存时,这种能力就丧失了。 一旦完成,新的WGF将使基地能够储存核远程防区外巡航导弹( ALCM),以供B-52运输。
Nuclear Bomber Force Increase
核轰炸机部队增加
The B-21 bomber program is expected to increase the overall size of the US strategic bomber force. The Air Force currently operates about 158 bombers (62 B-1B, 20 B-2A, and 76 B-52H) and has long said it plans to procure at least 100 B-21 bombers. That number now appears [https://www.airforcemag.com/article/strategy-policy-9/] to be at least 145, which will increase the overall bomber force by 62 bombers to about 220. There are currently nine bomber squadrons, a number the Air Force wants to increase to 14 (each base has more than one squadron).
B-21轰炸机计划有望增加美国战略轰炸机部队的整体规模。美国空军目前运营约158架轰炸机(62架B-1B,20架B-2A和76架B-52H),并长期以来表示计划采购至少100架B-21轰炸机。这个数字现在出现了[https://www.africemag.com/article/strategy-policy-9/]至少达到145架,这将使轰炸机总兵力增加62架,达到220架左右。目前有9个轰炸机中队,美国空军希望将这个数字增加到14个(每个基地有多个中队)。
During an interview with reporters in April, the head of AFGSC, General Timothy Ray, reportedly said the 220 number was a “minimum, not a ceiling” and added: “We as the Air Force now believe it’s over 220.” Whether Congress will agree to pay for that many B-21s remains to be seen.
据报道,美国空军全球打击司令部(AFGSC)负责人蒂莫西·雷(Timothy Ray)将军在4月份接受记者采访时说,220架的数量是“最小的,不是上限”,并补充说:“我们现在空军认为我们的数量已经超过220架。”国会是否会同意支付那么多B-21还有待观察。
The fielding of large numbers of nuclear-capable B-21 bombers has implications for the future development of the US nuclear arsenal. Under the New START treaty, the United States has declared it will deploy no more than 60 nuclear bombers. Although the treaty will lapse in 2026 (after a five-year maximum extension), it serves as the baseline for long-term nuclear force structure planning.
大量具有核能力的B-21轰炸机的部署对美国核武库的未来发展具有影响。根据新的《削减战略武器条约》,美国宣布将部署不超过60架核轰炸机。尽管该条约将于2026年失效(最长延期五年),但它可作为长期核武力结构规划的基准。
Unless the Air Force limits the number of nuclear-equipped B-21 bombers to the number of B-2As operated today, the number of nuclear bombers would begin to exceed the 60 deployed nuclear bomber pledge by 2028 (assuming an annual production of nine aircraft and two-year delay in deployment of the first nuclear unit). By 2035, the number of deployed nuclear bombers could have doubled compared with today (see graph below):
除非美国空军将配备核能的B-21轰炸机的数量限制为今天操作的B-2A的数量,否则到2028年,核轰炸机的数量将开始超过部署60架核轰炸机的承诺(假设每年生产9架飞机,第一个核单位的部署推迟了两年。 到2035年,部署的核轰炸机的数量可能会比今天增加一倍(请参见下图):
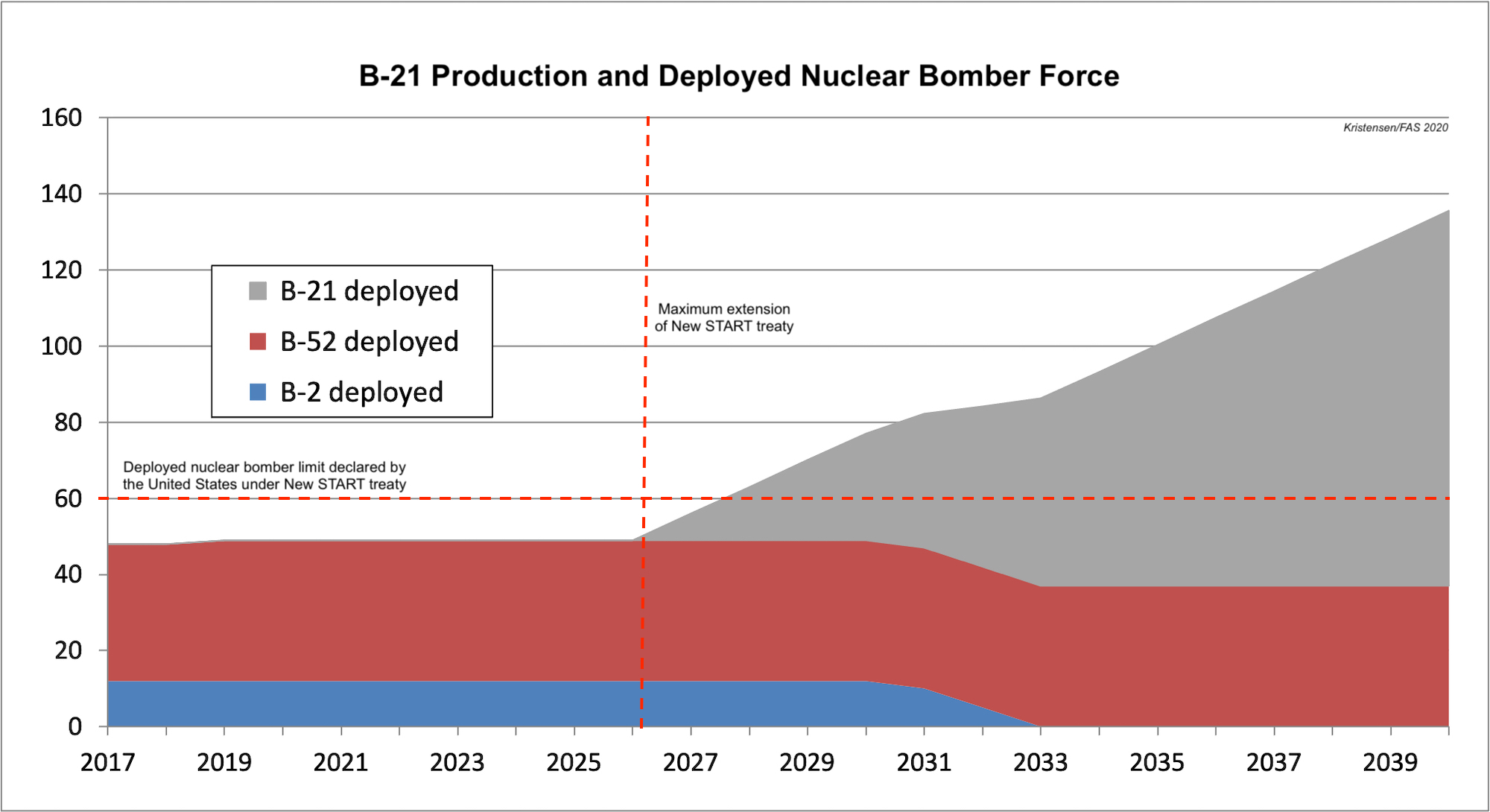
Unless nuclear B-21 bombers are not limited, the future nuclear bomber force could significantly exceed the bomber force under the current New START treaty.
除非核武B-21轰炸机不受限制,否则未来的核轰炸机力量可能大大超过目前新的《削减战略武器条约》规定的轰炸机力量。
It is difficult to imagine a military justification for such an increase in the number of nuclear bombers – even without New START. One would hope that the number of nuclear B-21s will be limited to well below the total number. Although the New START treaty would have expired before this becomes a a legal issue, it would already now send the wrong message to other nuclear-armed states about US long-term intensions, deepen suspicion and “Great Power Competition,” and could complicate future arms control talks.
即使没有新的《削减战略武器条约》,也很难想象军事上对增加核轰炸机数量的理由。人们希望核B-21的数量将被限制在远远低于总数的范围内。尽管新的《削减战略武器条约》在这成为一个法律问题之前就已经到期,但它现在已经向其他拥有核武器的国家发出了关于美国长期意图的错误信息,加深了猜疑和“大国竞争”,并可能使未来的军备控制谈判复杂化。
In the short term, the incoming Biden administration should commit the United States to not increase the number of nuclear bombers beyond those planned under the New START treaty, and it should urge Russia to make a similar declaration about the size of its nuclear bomber force.
在短期内,即将上任的拜登政府应承诺美国不要将核轰炸机的数量增加到新《削减战略武器条约》所计划的数量之外,并应敦促俄罗斯就其核轰炸机的规模做出类似的声明。
See also: Nuclear Notebook: US nuclear force, 2020
另见:核笔记本:美国核力量,2020年
This publication was made possible by generous contributions from the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation, the New Land Foundation, the Ploughshares Fund, and the Prospect Hill Foundation. The statements made and views expressed are solely the responsibility of the authors.
此文章发表是由约翰·D·和凯瑟琳·T·麦克阿瑟基金会、新土地基金会、犁铧基金会和展望山基金会慷慨捐助而成的。所作的陈述和发表的意见完全由作者负责。
上一篇:Going Big Time With Class D 下一篇:Trump Administration Again Refuses To Disclose Nuclear Weapons Stockpile Size
| The Booker dilemma: inside US Army transformation
“布克”困境:美国陆军转型内幕 |
| The decision to cancel the M10 Booker light tank is at the core of a reordering of US Army planning.... [2025-07-16] |
| Focus: A fragile balance in Asia, China has become leading military power in the
焦点:亚洲平衡脆弱,中国已成为该地区的主要军事力量 |
| However, China's rapid military growth in this area is tipping the balance in favor of regional power. ... [2024-08-27] |
| Small drones will soon lose combat advantage, French Army chief says
法国陆军总司令表示,小型无人机将很快失去战斗优势 |
| By Rudy Ruitenberg Thursday, Jun 20, 2024 作者:鲁迪瑞滕伯格 2024年6月20日星期四 French Army Chief of Staff Gen. Pierre Schill inspecting a Rapid Eagle anti-drone system at the Eurosatory defense show in Paris on June 19, 202... [2024-08-18] |
| What’s next for Ukraine’s incursion into Russia?
乌克兰入侵俄罗斯的下一步是什么? |
| Ukraine’s forces have surprised us all with its recent incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast since the operation to turn the tide of the war,... [2024-08-17] |