| Bluffer’s Guide: Fortress China[B]
布拉夫手册:中国堡垒[B] Date:2010-01-05 Source:环球网博客 By:无定河边骨 Viewed: |
3. Tactical systems / 战术防空系统
The Chinese military, including curiously the armed police (PAP), deploy a wide variety of short-ranged air defence systems. Some are fixed-site but most are operated in a truly mobile fashion.
在中国军队中,很奇怪地包括武警部队在内,都部署了大量各种型号的近程防空系统。它们当中的有些部分是采用固定发射阵地,但绝大多数则是使用完全机动的形式。
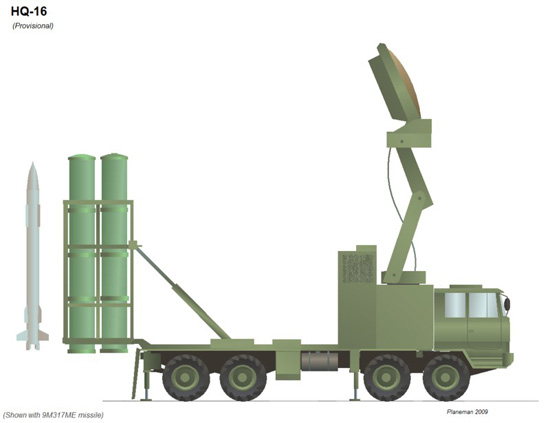
HQ-16
No such system has been confirmed but the ship-based version is believed to be fitted to the Type-054A frigates. Probably a close relative to the Russian SA-17 "Grizzly" system but vertical launched and possibly using the 9M317ME missile. The missile is about the same size as the HQ-9 but being hot-launched would have a shorter missile container. A truck with suspected HQ-16 tubes was photographed. A basic 8-wheel truck can comfortably mount 6 (3 wide by 2 high) of missiles so a TEL is likely to carry six missiles. The missiles are semi-active radar homing and would have a range of about 50km (similar to HQ-12).
没有如此系统曾经被确认过但是舰-载型据信装配在054A型护卫舰。或许接近俄国SA-17“灰熊”系统但垂直发射并可能使用9M317ME导弹。导弹大概如同HQ-9一样的尺寸但热-发射将会有一个较短的导弹容器。一辆卡车和可疑的HQ-16发射管已经被拍照。一辆8-轮卡车能足够装载6枚(横3枚2列)导弹,所以一辆TEL可能携带六枚导弹。导弹是半-主动雷达制导而且射程大约50公里(类似HQ-12)。

SA-15 ‘Tor’ / SA-15“道尔”
China purchased a modest number of SA-15 systems in the 1990s. Typically quoted number is 36 systems. Some sources speculate that China may be license producing the type. The SA-15s in Chinese service are the M1 standard.
中国于上世纪90年代采购了一定数量的SA-15防空系统。有消息称具体的数量为36套。还有一些消息来源推测中国可能得到了该型号的生产授权。在中国服役的SA-15的型号相当于M1改进型。
The launcher is completely self-sufficient with both surveillance and tracking/targeting radars on-mount, together with 8 vertically launched missiles.
发射车自身装备了整套监视与跟踪/目标指示雷达,共有8枚垂直发射的导弹。
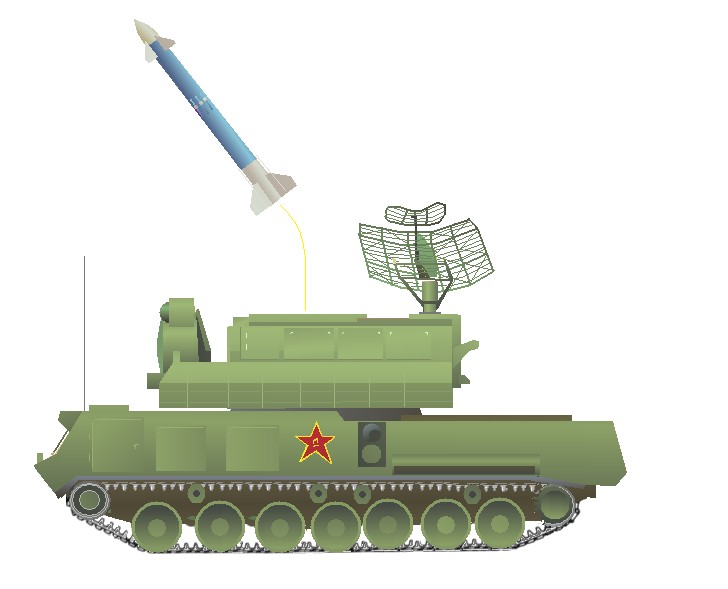
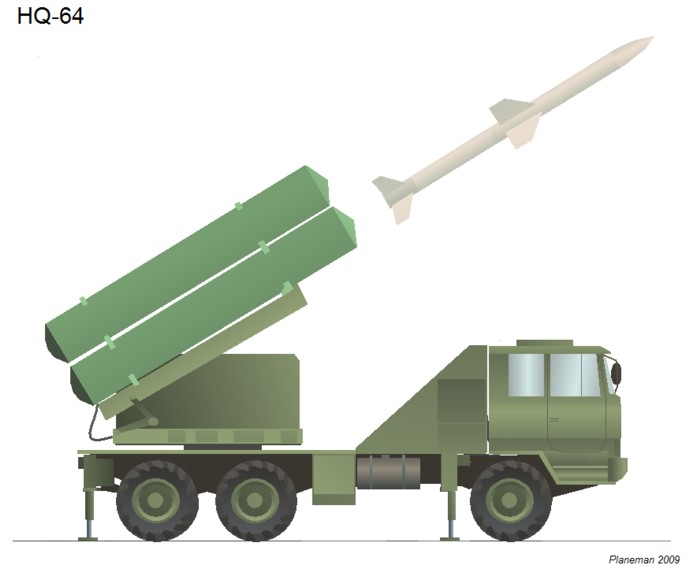
HQ-64 (LY-60)
This is an indigenous system developed from the older HQ-61. The missile is based on the Italian Aspide which itself is a development of the Sparrow missile. The HQ-64 was widely publicized in the 1990s (together with the HQ-9 and KS-1), but only recently appears to have entered Chinese service. The Air Force (PLAAF) deploys the system, and possibly the army (PLA) also.
这一型号是在老式的红旗61型基础上发展研制的国产防空系统。所使用的导弹是基于意大利“阿斯派”导弹改进的,而“阿斯派”导弹本身则是源自“麻雀”导弹。红旗64型在上世纪90年代曾被广为宣传(同时还有红旗9型和凯山1型),但是直到最近才开始加入现役。中国空军(PLAAF)部署了该系统,陆军(PLA)可能也装备了该系统。
A typical battery follows the HQ-61 model with a single surveillance radar serving up to three fire-control radars, each able to direct two 4-round launchers. All components are truck mounted for good mobility.
一个标准的红旗61导弹连配备一台监视雷达和三部火控雷达,每部火控雷达可以为两部装载4发导弹的发射车提供引导。所有的组件都使用卡车索引以获得良好的机动能力。
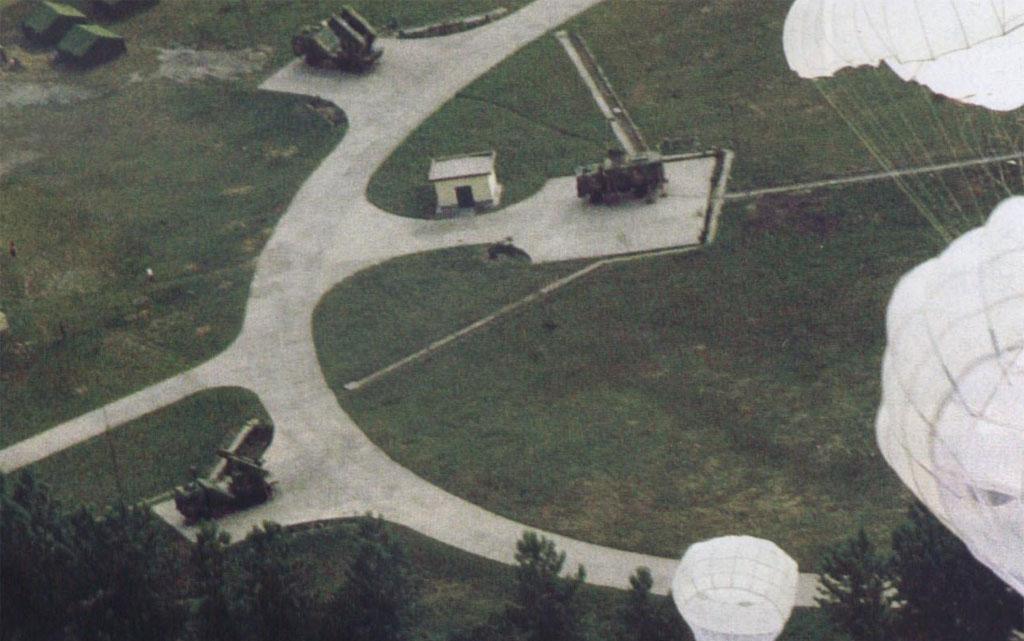
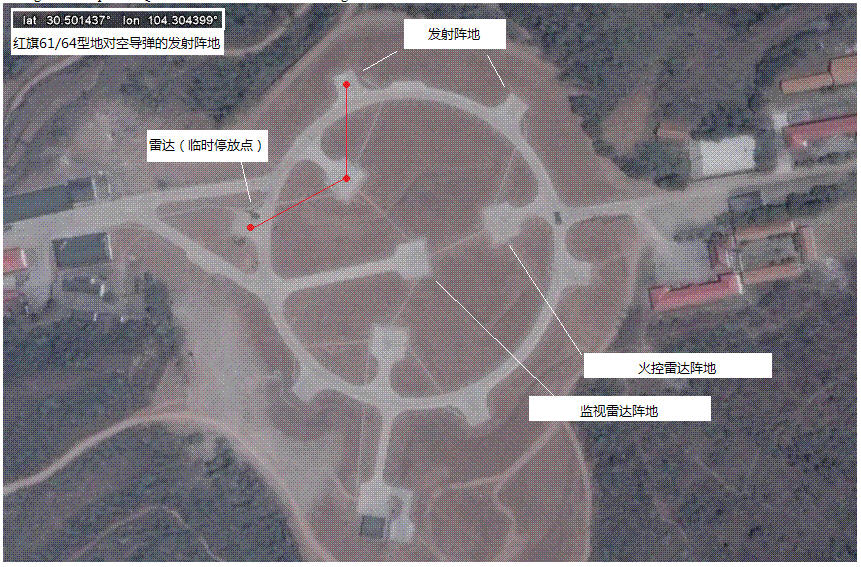
A single unoccupied HQ-6x site has been found on Google Earth:
在GoogleEarth上找到的一个闲置的红旗6x系列的发射阵地。
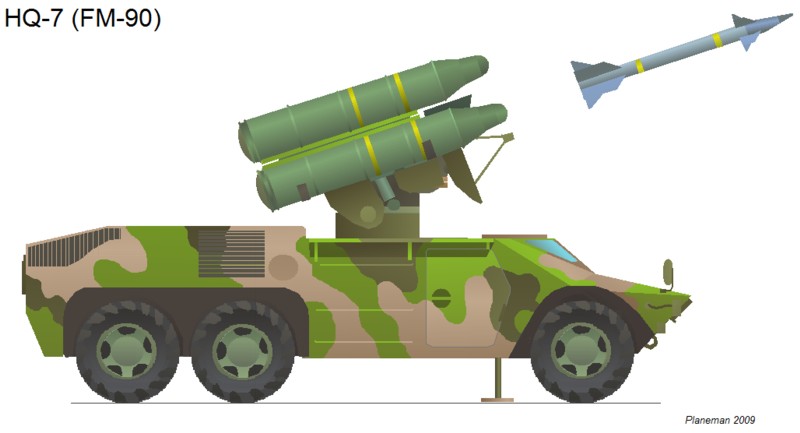
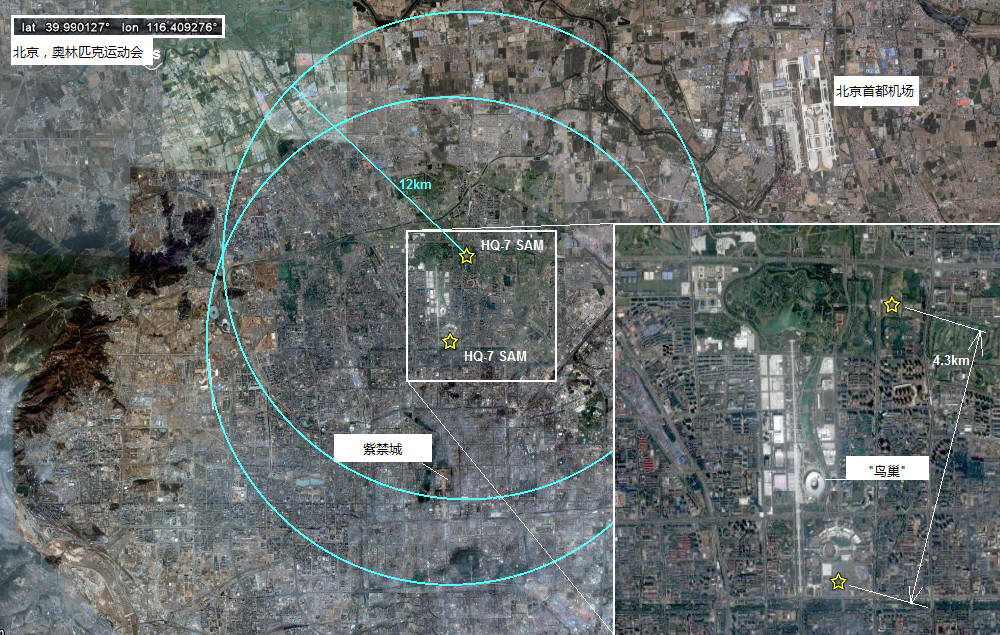
HQ-7 / 红旗7型
A Chinese copy of the French Crotale system, the HQ-7 is deployed by both the army and air-force. The system is highly mobile even in its towed ‘shelter’ version. The basic system has a range of 12km and provides modest defense against fast jet targets. The PLAAF shelter version:
法国“响尾蛇”系统的中国版本,红旗7型由陆军和空军共同研制。尽管该系统采用的是拖挂的形式,其机动性能依然相当的高。其标准型系统的射程达到12公里,对于快速的喷气式目标具有相当的防御能力。下图是中国人民解放军拖车版的红旗7型:
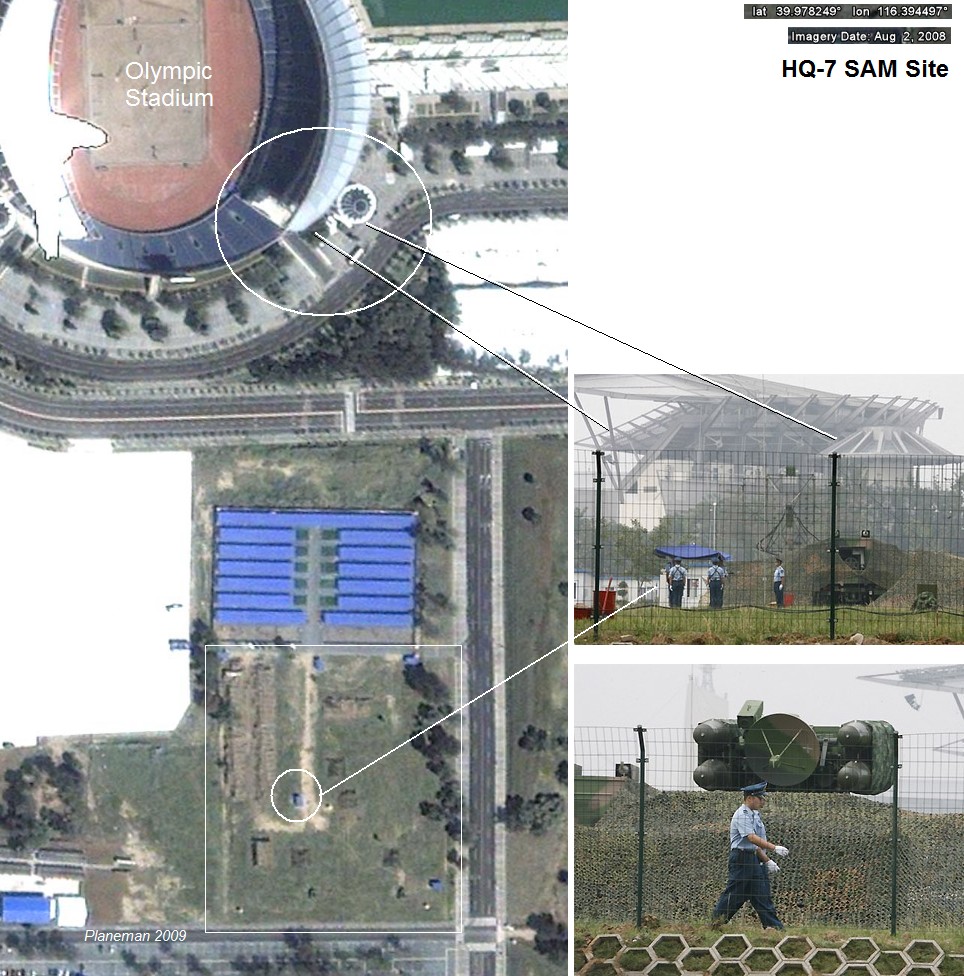
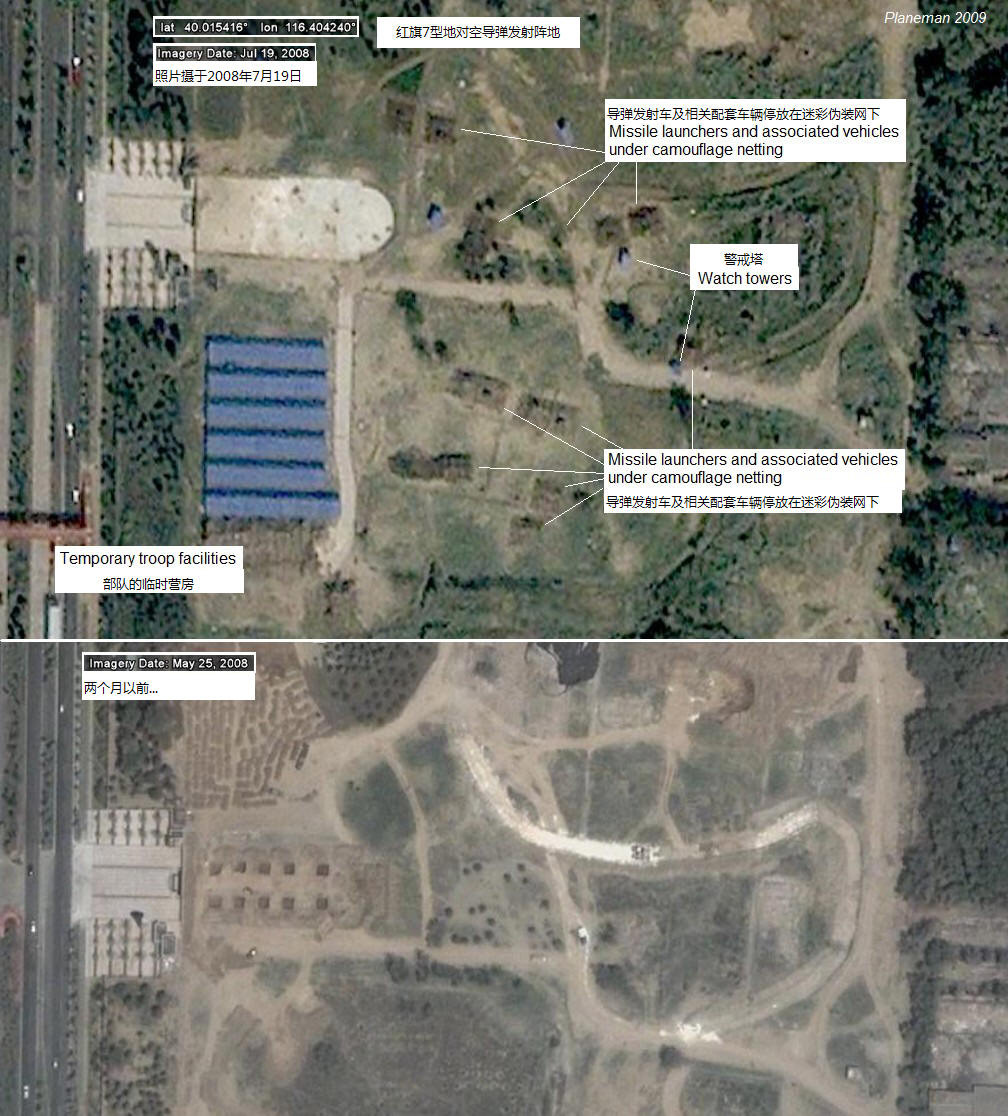
Finding HQ-7 units deployed on Google Earth is virtually impossible due to their mobile nature and the adoption of camouflage nets, but the PLAAF deployed two batteries to protect the Olympic games and one of these was widely publicized. By chance it is caught on Google Earth and I also found the other battery. Although there are a few trappings of a comfortable holiday period token deployment, the sites nonetheless give rare insight into HQ-7 site layouts:
由于红旗7型的的机动能力和迷彩伪装网的使用,想要在GoogleEarth上找到它们事实上的可能性是不存在的,但是为了保卫奥林匹克运动会的召开中国人民解放军为之部署了两个红旗7型导弹阵地,其中的一个还被广泛宣传。GoogleEarth抓住了这次机会,而我也找到了另一个未被公开的发射阵地。尽管在部署之前采取了一些迷彩伪装的手段和措施,但还是给了我们一次全面了解红旗7型发射阵地布局的机会:
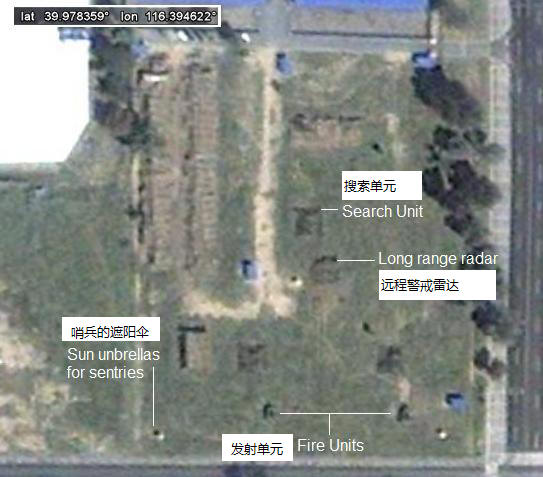
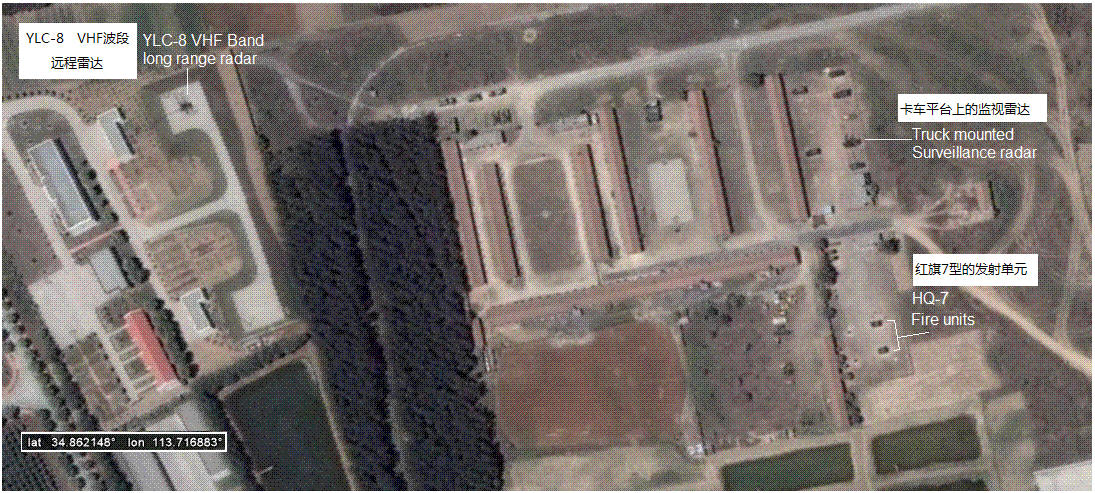
Another HQ-7 site at an air base:
位于一个空军基地中的另一个红旗7型发射阵地:
China has developed successive improved versions of the HQ-7 with numerous prototypes and models at defense shows. The latest version, with an export designation FM-90 (In-service designation not known but logically HQ-7C), appears to have entered limited service. The FM-90 features a longer ranged missile (15km vs 12km) and a new six wheel launch vehicle:
中国已经成功研制出红旗7型的改进版本并在一些展会上展出了大量原型资料及模型。其中最新改进版本的出口型号为飞蠓90(其服役型号的代号尚未公开,但按习惯应该是红旗7C型),并且似乎已经少量服役。飞蠓90的特点在于有更大的射程(从12公里提高到15公里)并且使用的是新型的6轮发射车:
A single FM-90 site has been found on Google Earth by Sean O’Connor. The site itself is clearly originally an HQ-2 site so the layout should not be regarded as typical for HQ-7:
肖恩·欧康纳在GoogleEarth上找到了一个飞蠓90的发射阵地。这个发射型地本身很显然是从红旗2型的发射阵地改建而来,因此不能认为是典型的红旗7型发射阵地。
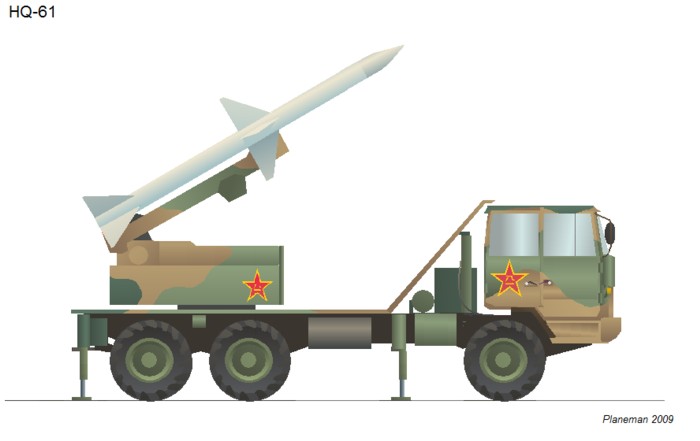
HQ-61 / 红旗61
The oldest indigenous SHORAD to be in service, the HQ-61 is now obsolete. The missile is similar in appearance to the Sparrow but is slightly larger and has the forward fins out-of-line to the rear fins. Range is about 10km. It is reportedly only used in Beijing military region but I suspect it is deployed in Shanghai also (see Google Earth below).
做为现役当中服役时间最长的国产近程防空系统,红旗61现在已经过时了。这种导弹在外形上与麻雀导弹很相似,但要稍稍更大一些,并且在前翼和尾翼之间有线条状凸起。其射程大约为10公里。据说该型号只在北京军区范围内使用,但我猜想在上海也会部署该系统(参见下面的GoogleEarth图)。
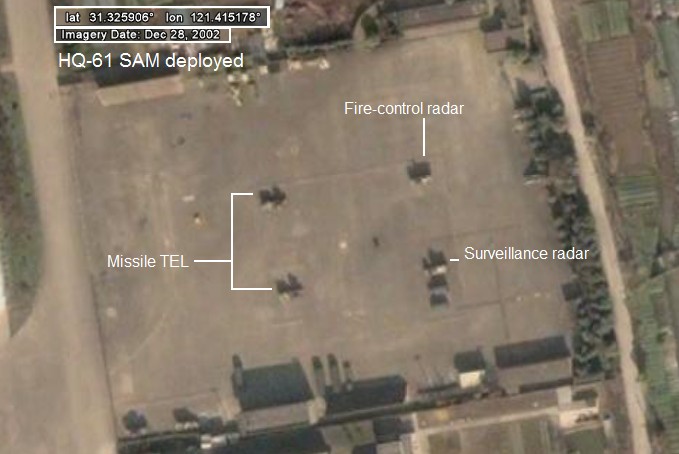
A single ‘field’ deployment is visible in historic data on Google Earth:
唯一可以在GoogleEarth的历史图片上找到的战备状态图:
上一篇:Bluffer’s Guide: Fortress China[A] 下一篇:Bluffer’s Guide: Fortress China[C]
| The Booker dilemma: inside US Army transformation
“布克”困境:美国陆军转型内幕 |
| The decision to cancel the M10 Booker light tank is at the core of a reordering of US Army planning.... [2025-07-16] |
| Focus: A fragile balance in Asia, China has become leading military power in the
焦点:亚洲平衡脆弱,中国已成为该地区的主要军事力量 |
| However, China's rapid military growth in this area is tipping the balance in favor of regional power. ... [2024-08-27] |
| Small drones will soon lose combat advantage, French Army chief says
法国陆军总司令表示,小型无人机将很快失去战斗优势 |
| By Rudy Ruitenberg Thursday, Jun 20, 2024 作者:鲁迪瑞滕伯格 2024年6月20日星期四 French Army Chief of Staff Gen. Pierre Schill inspecting a Rapid Eagle anti-drone system at the Eurosatory defense show in Paris on June 19, 202... [2024-08-18] |
| What’s next for Ukraine’s incursion into Russia?
乌克兰入侵俄罗斯的下一步是什么? |
| Ukraine’s forces have surprised us all with its recent incursion into Russia’s Kursk Oblast since the operation to turn the tide of the war,... [2024-08-17] |