| HQ-7 (FM-80) SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM
中国HQ-7(FM-80)防空导弹系统 Date:2017-01-07 Source:Internet By:Globalmil Viewed: |

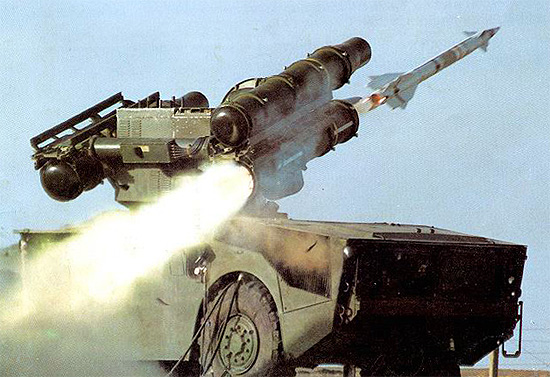
The HQ-7 is a Chinese copy of the French Thales Air Defence (formerly Thomson-CSF Airsys) Crotale air defence missile system. It is China’s first modernised low- and very low-altitude air defence system.HQ-7是法国泰利斯防空公司(以前的汤姆森-CSF Airsys公司)Crotale防空导弹系统的一个中国仿造型。它是中国最早的现代化低空和超低空防空系统。
The HQ-7 (also known as FM-80 in its export form) is an all-weather short range air defence system developed by 2nd Aerospace Academy (now China Academy of Defence Technology) on the basis of the French Crotale air defence missile. The HQ-7 entered operational service in the late 1980s with the PLA ground forces and PLA Air Force (PLAAF) to provide short-range point defence. The improved variant FM-90 was introduced in 1998.
中国HQ-7(外销型被称为FM-80)是一种全天候近程防空导弹系统,以法国Crotale导弹为基础,由中国第二宇航研究所(现在中国防卫技术研究院)发展。在1980年后期进入PLA操作服役,为PLA地面部队和PLA空军 (PLAAF)提供近程点防御。改良型FM-90在1998年被推出。
PROGRAMME
计划
The development of the HQ-7 surface-to-air missile (SAM) began in 1979 to meet a requirement of the PLA for a mobile, short-range, low- and very low-altitude air defence system. The programme was managed by the 2nd Aerospace Academy (also known as China Changfeng Mechanics and Electronics Technology Academy, now China Academy of Defence Technology). 23 Institute was responsible for the development of radar fire control system, and 206 Institute was responsible for the ground equipment.
HQ-7防空导弹(SAM)的发展在1979年开始,去符合PLA的一个需求用于机动、近程、低和超低空防空系统。 计划由第二航宇研究所负责(也即是中国Changfeng力学和电子学技术学院,现在中国防卫技术学院),23所负责雷达火控系统的发展和206所负责地面设备。
The HQ-7 is almost identical in physical and technical characteristic to the French Thales Air Defence (formerly Thomson-CSF Airsys) Crotale air-defence missile system. China imported few examples of Crotale and its shipborne version Sea Crotale in the late 1970s when it formed an alliance with Western countries against the Soviet Union. Thomson-CSF was expecting more orders to follow but China developed its own version by reverse-engineering the examples it obtained. This was probably tolerated or even tacitly consented by the French government in exchange for China’s co-operation in the Cold War.
HQ-7几乎在实际上和技术上与法国泰利斯防空公司(以前的汤姆森-CSF Airsys)Crotale防空导弹系统相同的。中国在1970年后期进口了少量的Crotale和它的舰载型Sea Crotale,当时中国为对抗前苏联和西方国家形成一个同盟。汤姆森-CSF公司正在期待更多后继订购,但是中国对该导弹进行了反向-工程学,获得它自己的版本。可能法国政府为在冷战中获得中国的合作,对此容忍和默认。
Test missiles were made in 1983 and the first firing took place in 1985. Design certification was undertaken from July 1986 to June 1988. Production began shortly afterwards for use as filed air defence. The HQ-7 is available in two versions; the shelter-mounted version used by the PLAAF and self-propelled version used by the PLA ground forces. The export version FM-80 was first revealed in the 1989 Dubai Aerospace Show. Later in 1998 China National Precision Machinery Import and Export Corporation (CNPMIEC) introduced an improved variant FM-90 featuring fast and longer-range missile and infrared camera to compliment the TC tracking camera.
导弹测试在1983年进行和在1985年进行第一次发射试验。设计认证从1986年7月到1988年6月着手。生产后不久开始使用被当做战场防空。HQ-7可获得二种型号:PLAAF使用的舰载箱体安装型;PLA地面部队使用的自行机动型。出口型FM-80在1989年迪拜宇航展中被首次展示。稍后在1998年中国国家精密机械进出口公司(CNPMIEC)介绍一种改进型FM-90,具有高速和更大射程的特点,红外线摄相机去补充TC跟踪摄像机。

The HQ-7 is available in two versions: the shelter-mounted version used by the PLAAF (shown in this photo), and self-propelled version used by the PLA ground force.HQ-7可获得的二种型号:PLAAF(在这一张相片中显示)使用的箱体安装型;PLA地面部队使用的机动自行型。
MISSILE
导弹
导弹
The HQ-7 missile features a long, slim body with sharp nose, four stabilisation fins, and four front canards. The missile has multi-target interception capabilities to engage targets from same or different directions. Using a solid rocket motor, the missile has a max speed of Mach 2.3 and a range of 12km. The Command to Line Of Sight (CLOS) guidance uses radar and electro-optical sensors. Guidance operating modes include IR, IR+TV, and manual, with robust resistance to active/passive jamming and meteorological noises. The missile is armed with a high-explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) warhead, initiated by with a proximity fuse.
HQ-7导弹的特点以一个长瘦形弹体、锥形前端、四个稳定翼片和四个前鸭翼片为特点。导弹具有多目标拦截能力去与自相同或不同方向的目标交战。采用固体火箭发动机,导弹最大飞行速度Mach 2.3和射程12公里。瞄准线指令(CLOS)制导使用雷达和光电传感器。制导操作模块包括IR、IR+电视和手控,稳定性强能对抗主动/被动干扰和气象噪音。导弹装有高爆破片(HE-FRAG)弹头,使用近炸引信启动。
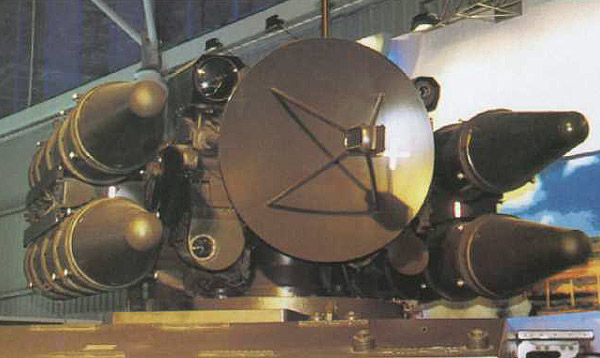
The HQ-7 missile is armed with a high-explosive fragmentation (HE-FRAG) warhead, initiated by with a proximity fuse.HQ-7导弹装有一个高爆破片(HE-FRAG)弹头,采用近炸引信启动。
FIRE-CONTROL & SURVEILLANCE
火控和监视
A typical HQ-7 operational battalion comprises three operational sections (batteries) and a technical support section (battery), with both direct support (10 vehicles) and indirect support (with various special test benches and standard test equipment) maintenance groups. Each battery comprises a Search Unit (SU), three Firing Units (FUs), three optical aiming systems, and four 40kW generators.
典型的HQ-7操作营包含三个操作部门(连)和一个技术支援部门(连),以及对两者直接支援(10部车辆)和间接支援(使用各种不同的特别测试工作台和标准测试设备)维护组。每个连包括一个搜索单元(SU),三个发射单元 (FUs),三套光学瞄准目标系统和四台40千瓦发电机。
The HQ-7's search unit is used to search, identify, evaluate, and classify the targets. It then designates the most dangerous targets and distributes the information to the firing unit(s). If the radar is jammed then the optical aiming units of firing units can be used to acquire and designate targets.
HQ-7搜索单元用来搜索、识别、评估和目标分类。然后指定最危险的目标和分配信息到发射单元。如果雷达被阻塞,那么发射单元的光学瞄准单元能用来去捕获和指定目标。
The search unit comprises a E/F-band Doppler search radar which has a detection range of 3,200m to 18,400m; a data processing unit capable of process 30 targets and in conjunction with the radar system to track 12 targets simultaneously; a wire network between itself and firing units; IFF, and radio station.
搜索单元包括一部E//F波段多普勒搜索雷达,探测距离3,200 米到18,400 米;一个数据处理单元能够处理30个目标,连接雷达系统内去同时追踪12个目标;在它自身和发射单位之间采用导线网络连接;IFF和无线电台。

The search unit comprises a E/F-band Doppler search radar which has a detection range of 3,200m to 18,400m; a data processing unit capable of process 30 targets and in conjunction with the radar system to track 12 targets simultaneously; a wire network between itself and firing units; IFF, and radio station.搜索单元包括一部E/F波段多普勒雷达探测距离3,200米到18,400米;一套数据处理单元能够处理30个目标,连接在雷达系统内同时跟踪12个目标;它自身和发射单元之间的一个导线网络;IFF和无线电台。
The firing unit comprises a four- or eight-cell missile launcher; a monopulse J-band tracking radar with an operational range up to 17,000m; a TV tracking system with an operational range of over 15,000m in clear weather; an infra-red localiser; a data processing unit; a wire network between itself, the search unit, and other firing units.

The firing unit comprises a four-cell missile launcher; a monopulse J-band tracking radar with an operational range up to 17,000m; a TV tracking system with an operational range of over 15,000m in clear weather; an infra-red localiser; a data processing unit; a wire network between itself, the search unit, and other firing units.发射单元包括一套四单元导弹发射装置;一部单脉冲 J-波段操作距离达到17,000 米的跟踪雷达;一套电视跟踪系统,操作距离在晴朗天气15,000米;红外定位器;一套数据处理单元;它自身、搜索单元和其它发射单元之间的一个导线网络。
发射单元包括一个四或八单元导弹发射装置;一部单脉冲J-波段跟踪雷达具有操作范围达到17,000米;一部电视跟踪系统具有操作范围在晴朗天气下15,000米;红外定位器;一套数据处理单元;导线网络连接它自身、搜寻单元和其它的发射单元。

The firing unit comprises a four-cell missile launcher; a monopulse J-band tracking radar with an operational range up to 17,000m; a TV tracking system with an operational range of over 15,000m in clear weather; an infra-red localiser; a data processing unit; a wire network between itself, the search unit, and other firing units.发射单元包括一套四单元导弹发射装置;一部单脉冲 J-波段操作距离达到17,000 米的跟踪雷达;一套电视跟踪系统,操作距离在晴朗天气15,000米;红外定位器;一套数据处理单元;它自身、搜索单元和其它发射单元之间的一个导线网络。
The self-propelled version HQ-7 is mounted on a P4R electricity-powered wheeled 4 X 4 chassis, which has a maximum road speed of 60km/h and a max range of 500km.
机动自行式HQ-7安装在一部P4R电动轮式4X4车底盘上,最大道路速度60公里/小时和最大行程500公里。
FM-90
飞蠓-90
飞蠓-90

The FM-90 is an improved version featuring fast and longer-range missile and infrared camera to compliment the TC tracking camera.FM-90是一种改进型,特点是高速和更远射程,红外摄像机去补充TC跟踪摄像机。
At the end of 1998, the FM-90, an enhanced version of the FM-80/HQ-7, was introduced to the public. Compared to the original system, the improvements on the FM-90 include:
在1998年底,FM-90,一种FM-80/HQ-7的增强型号,公开展示。与最初的系统相对比,在FM-90上的进步包括:
Using VLSI technology-based computer (designed by 706 Institute) to replace the original LSI technology-based S-9 computer on the HQ-7/FM-80.
Using digital electronic technology to replace the original analogue design, increasing the missile's abilities against active/passive jamming.
Using a new two-waveband tracking radar to replace the original monopulse radar
An infrared camera was added to the TV tracking system so that the optical tracking system can be used at night.
Target information between search and firing units is transmitted via a datalink pole system similar to that fitted on the later production Thomson-CSF Crotale 4000.
Re-designed missile warhead fusing system.
In addition, the missile's seeking/homing range, maximum speed, and attack range all have been improved, which greatly increases its combat effectiveness. With a maximum detecting range of 25km, the FM-90 is capable of attacking three targets using three different guidance modes simultaneously. The missile also has anti-missile ability against ultra-low-altitude cruise missiles, air-to-surface missiles, and anti-radiation missiles at a distance of 17km.
使用“超大规模集成技术”(VLSI技术)-基于计算机 (由706所设计)代替最初的“大规模集成技术”(LSI 技术)-基于HQ-7/FM-80上的S-9计算机。
使用数字电子技术代替最初的模拟设计,增加对抗主动/被动干扰能力。
使用一部新的双-波段跟踪雷达代替最初的单脉冲雷达。
一部红外线摄像机增加到电视跟踪系统,以便光学跟踪系统能在夜晚使用。
目标在搜索和发射之间的信息传输经由一个数据链节点系统,与稍后安装生产的汤姆森-CSF Crotale 4000类似。
重新设计了导弹弹头引信系统。
除此之外,导弹搜索/导引距离,最大加速度和攻击距离已经被全部改良,大幅地增加它的战斗效能。最大探测距离25 公里,FM-90能够同时使用三个不同的引导模式攻击三个目标。导弹能在17公里距离对抗超低高度巡航导弹、空对地火箭和反辐射导弹。
SPECIFICATIONS
规格
Missile dimensions: (length) 3.00m; (diameter) 0.156m; (wingspan) 0.55m
Launch weight: 84.5kg
Operating altitude: 30~5,000m (HQ-7/FM-80); 15~6,000m (FM-90)
Minimum operating range: 500m (HQ-7/FM-80); 700m (FM-90)
Max operating range: 8,600m (400m/s target); 10,000m (300m/s target); 12,000m (helicopter); FM-90: 15,000m to all targets
Speed: Mach 2.3 (750m/s)
Guidance: Command + electro-optical tracking
Warhead: HE-FRAG with proximity fuse
Single shot hit probability: 70~80%
Radar detecting range: (HQ-7/FM-80) 18.4km; (FM-90) 25km
Radar homing range: (HQ-7/FM-80) 17km; (FM-90) 20km
导弹尺寸:(长度)3.00 米;(直径)0.156 米;(翼展)0.55 米
发射重量: 84.5 公斤
操作高度: 30~5,000 米(HQ-7/FM-80);15~6,000 米(FM-90)
最小操作距离: 500 米(HQ-7/FM-80);700 米(FM-90)
最大操作距离: 8,600 米(400 米/秒目标);10,000 米(300 米/秒目标);12,000 米(直升飞机);FM-90: 对所有的目标 15,000 米
速度: Mach 2.3(750 米/秒)
制导: 指令+光电跟踪
弹头: HE-FRAG和近炸引信
单发攻击概率: 70~80%
雷达探测距离: (HQ-7/FM-80)18.4 公里;(FM-90)25 公里
雷达导引距离: (HQ-7/FM-80)17 公里;(FM-90)20 公里
上一篇:HQ-9 (FT-2000) SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM 下一篇:KS-1 SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM
| HQ-3(Hongqi-3)Air defense missile
中国“红旗”(HQ-3,Hongqi)-3号防空导弹 |
| Hongqi-3 missile weapon system had incorporated a lot of newly developed items. 28 organizations which participated the work were from the 1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 7th Ministries of Machine Building and Air Force. Actually the country wide coo... [2020-04-06] |
| KS-1 SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM
中国“凯山”(KaiShan)-1(KS-1)地对空导弹系统 |
| The KaiShan-1 (KS-1) is a medium- to long-range, all-altitude surface-to-air missile system developed by China Academy of Defence Technology (CADT).... [2017-01-07] |
| HQ-7 (FM-80) SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM
中国HQ-7(FM-80)防空导弹系统 |
| The HQ-7 (also known as FM-80 in its export form) is an all-weather short range air defence system developed by 2nd Aerospace Academy (now China Academy of Defence Technology) on the basis of the French Crotale air defence missile. ... [2017-01-07] |
| HQ-9 (FT-2000) SURFACE-TO-AIR MISSILE SYSTEM
中国红旗(HQ)-9型(FT-2000)地对空导弹系统 |
| The HongQi-9 (HQ-9) is a long-range, all-altitude, all-weather surface-to-air missile system to counter aircraft, helicopters, and cruise missiles. It also has limited capabilities against tactical ballistic missiles.... [2016-08-14] |
