| Hammer and shield: Russia's modernised radar and early warning systems
锤子和盾牌:俄罗斯的现代化雷达和预警系统 Date:2022-03-12 Source:janes By:Naqi Wasif Viewed: |
25 FEBRUARY 2022
by Naqi Wasif
2022 年 2 月 25 日
纳奇·瓦西夫
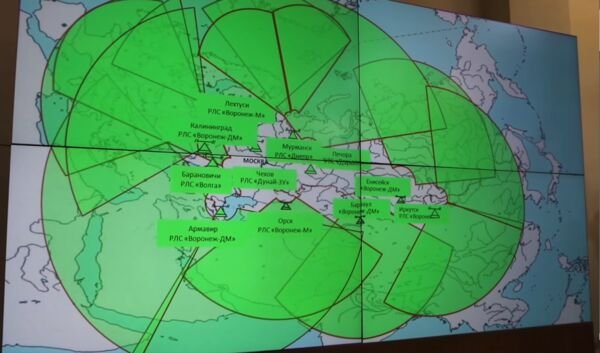
Russian ABM radar coverage from long-range systems is shown in this screenshot from a news article on the main missile warning centre in Moscow posted by the Russian Ministry of Defence on 16 February 2022. (mil.ru)
俄罗斯国防部于2022年2月16日发布的有关莫斯科主要导弹预警中心的新闻文章截屏显示了俄罗斯远程系统的反导雷达覆盖范围。 (mil.ru)
The large-scale movement of Russian forces into positions near its border with Ukraine and into Belarus' territory included the Russian Armed Forces' latest air- and missile-defence capabilities, which have become a key component in its military doctrine after the significant modernisation of capabilities.
俄罗斯军队向乌克兰边境附近的阵地和白俄罗斯领土的大规模调动包括俄罗斯武装部队最新的防空和导弹防御能力,这些能力在俄罗斯实现重大现代化后已成为其军事理论的关键组成部分。
Following a brief period of restructuring in 1997, Russia's air defence forces were realigned to the legacy role of denying adversaries air superiority through strategic deterrence, as well as offering mobile support for ground elements, and maintaining anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) readiness. This has been achieved through an integrated and layered sensor network for air- and anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defence that operates across an extensive command-and-control (C2) infrastructure.
在1997年进行了短暂的重组后,俄罗斯的防空部队被重新调整为通过战略威慑阻拒对手空中优势的传统角色,以及为地面部队提供机动支援,并保持反介入/区域拒止 (A2/AD) ) 准备。这是通过用于空中和反弹道导弹 (ABM) 防御的集成和分层传感器网络实现的,该网络在广泛的指挥和控制 (C2) 基础设施中运行。
Command and conquer
指挥与控制
The Federal System for Aerospace Reconnaissance and Control (FSASRC) (Russian: FSR KVP) is operated by the Russian Air Force Radio-Technical Troops (RTV VKS) and is key to the air and space defence of the Russian Federation. Established in 1994 by a presidential decree, the FSR KVP is a combination of interrelated forces, facilities, and systems that work to deliver a consolidated, comprehensive, and real-time picture of the air environment. The FSR KVP is able to draw on civilian air traffic control (ATC) radar, military air surveillance radar networks – including monitoring identification friend-or-foe (IFF) and aircraft transponders – and dual-purpose electronic intelligence (ELINT) stations.
联邦航空航天侦察与控制系统(FSASRC)(俄语:FSR KVP)由俄罗斯空军无线电技术部队(RTV VKS)操作,是俄罗斯联邦空中和太空防御的关键。FSR KVP于1994年根据总统令成立,是相互关联的力量、设施和系统的组合,旨在提供综合、全面和实时的空中环境图景。FSR KVP能够利用民用空中交通管制(ATC)雷达、军用空中监视雷达网络——包括监测敌我识别(IFF)和飞机应答器——以及两用电子情报(ELINT)站。
The FSR KVP is a unified automated radar system that enables data exchange between civilian ATC and military air surveillance networks through a complex exchange for collection, processing, and distribution of data using the VIP-117M3 radar data pickup module.
FSR KVP是一个统一的自动雷达系统,通过使用VIP-117M3雷达数据采集模块收集、处理和分发数据的复杂交换,实现了民用ATC和军用空中监视网络之间的数据交换。
A typical VIP-117M3 mobile station uses high-speed data channels to maintain situational awareness across a 3,200 km 2 area for targets operating at a maximum altitude of 100 km. Commands can be issued to fighter interceptors for six to eight air targets via two navigator workstations. 3D ATC radar, such as the 12A6 Sopka-2, have been deployed countrywide in Russia and Belarus, and besides primary air surveillance capabilities they are fitted with both IFF Mk-X secondary surveillance systems and the successor to the Soviet ‘Parol' IFF system – the unified system of radar IFF (ES GRLO). In addition, the 48Ya6 Podlet mobile primary and secondary air surveillance radars are operated by the RTV VKS, providing a similar function in a deployable capacity.
典型的VIP-117M3移动站使用高速数据通道,在3200平方公里的区域内对最大高度为100公里的目标保持态势感知。可以通过两个导航工作站向战斗机拦截器发出针对6到8个空中目标的命令。3D ATC雷达,如12A6 Sopka-2,已在俄罗斯和白俄罗斯全国范围内部署,除主要空中监视能力外,还配备了敌我识别Mk-X二级监视系统和苏联 “口令”(Parol)敌我识别系统(IFF)的后继系统——雷达敌我识别统一系统(ES GRLO)。此外,48Ya6移动吊舱式一次和二次空中监视雷达由RTV VKS操作,以可部署的能力提供类似的功能。
The FSR KVP is undergoing its third phase of development since 2015, and includes subsystems for operations in the Arctic, as well as new radar sources for the detection and tracking of hypersonic and ballistic air targets. The Voronezh and Rezonans radar complexes are the latest radars to have been inducted into the system for tracking ballistic and hypersonic threats respectively. By the end of 2021, five 77Ya6 Voronezh and four 77Ya6-DM Voronezh-DM stations had been deployed around Russia to give all-round coverage, and five 69Ya6 Rezonans radars had been deployed in the Arctic Circle area to provide early warning of hypersonic air targets.
FSR KVP正在经历自2015年以来的第三阶段开发,包括用于北极地区作战的子系统,以及用于探测和跟踪高超音速和弹道空中目标的新雷达源。“沃罗涅日”(Voronezh)和“雷佐南斯”(Rezonans)雷达综合体是最新雷达在系统中分别用于跟踪弹道和高超音速威胁。截至2021年底,俄罗斯周边部署了五个77 YA6“沃罗涅日”和四个77 YA6 DM“沃罗涅日”雷达站,进行全覆盖,五个69YA6 ‘雷佐南斯“雷达部署在北极圈地区,为高超声速空中目标提供预警。
The Voronezh-M radar has a processing capacity of 100 billion operations/second, and the Rezonans computing system consists of a series of single-board quad-core seventh generation computers and uses artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the cognitive function of the radar for tracking hypersonic targets. The radars can simultaneously interface with command posts and automated control systems (ACS) of air-defence systems, in particular with the Polyana-D4M1 complex; VIP-117M3; Akatsiya; CP-1; Galaktika ATC integrated control system; HLCP-2; and the S-350, S-300, S-300V, and S-400 ground-based air-defence systems.
“沃罗涅日”-M雷达的处理能力为每秒1000亿次运算,“雷佐南斯”计算系统由一系列单板四核第七代计算机组成,并使用人工智能(AI)增强雷达跟踪高超音速目标的认知功能。雷达可以同时与防空系统的指挥所和自动控制系统(ACS)接口,尤其是与Polyana-D4M1综合体;VIP-117M3;Akatsiya;CP-1;Galaktika ATC综合控制系统;HLCP-2;以及S-350、S-300、S-300V和S-400陆基防空系统。
In Tor they trust
他们信任“道尔”
The Russian PVO SV (Air Defence Troops of the Ground Forces) provide mobile air-defence batteries in the Russian Army's areas of operation, with assets that range from Igla and Strela manportable air-defence systems (MANPADs) to ZSU-23-4 Shilka and the S-300V4.
俄罗斯PVO SV(地面部队的防空部队)在俄罗斯陆军的行动区提供移动式防空连,其资产范围从”针“式(Igla)和”箭“式(Strela)便携式防空系统(MANPADs)到ZSU-23-4”石勒喀河“ (Shilka)自行高炮和s-300V4防空导弹。
The 9S52M1 Polyana-D4M1 automated brigade command system can designate targets to air defence assets within two to three seconds and draws on inputs from up to three external and three ‘organic' radar sources. It can control up to six air defence battalions in a 1,600 km 2 area, and simultaneously maintain 500 tracks and 256 air targets. Targets with a maximum altitude of 51 km and travelling at speeds of up to 2.5 km/s can be assigned for engagement by Tor, Buk, and S-300V batteries via eight combat control and three planning workstations.
9S52M1 Polyana-D4M1自动化旅指挥系统可以在2到3秒内将目标指定给防空资产,并利用最多三个外部和三个“建制”雷达源的输入。它可以在1600平方公里的区域内控制多达6个防空营,同时维护500条航迹和256个空中目标。最高高度为51公里、速度高达2.5公里/秒的目标可通过八个作战控制和三个规划工作站,由“道尔”(TOR)、“山毛榉”(Buk)和s-300V防空连分配交战。
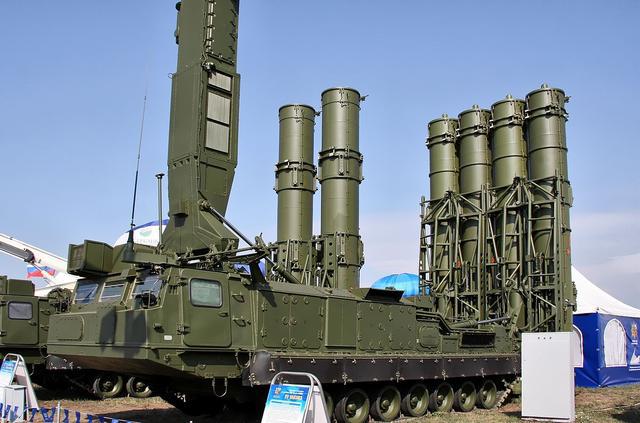

S-300V4
The S-300V4 (SA-12/23 Giant/Gladiator) operates at the highest level of mobile air defence in the PVO SV, and is unique in being the only fully mobile anti-intermediate and tactical ballistic missile and surface-to-air missile (SAM) system in the world. The S-300V was originally designed for detecting and tracking missile raids by the MGM-31 Pershing class of intermediate-range ballistic missiles (IRBMs), as well as the AGM-69 class of air-to-surface short-range attack missiles (SRAMs), and the Air-Sol Moyenne Portée/-Amélioré (ASMP/ASMP-A), including when operating under conditions of active radar jamming; the system employs semi-active radar homing (SARH) missiles.
S-300V4(SA-12/23 "巨人"(Giant)/"角斗士"(Gladiator))是PVO SV中最高级别的机动防空系统,是世界上唯一全机动的反中程和战术弹道导弹及地对空导弹(SAM)系统。S-300V最初设计用于探测和跟踪MGM-31潘兴级中程弹道导弹(IRBMs)、AGM-69级空对地短程攻击导弹(SRAM)和空射中程导弹(air Sol Moyenne Portée)/-Amélioré(ASMP/ASMP-A)的导弹袭击,包括在有源雷达干扰条件下运行时;该系统采用半主动雷达寻的(SARH)导弹。
Deployed at the battalion level, the S-300V4 is comprised of a target detection and designation unit (DDU) and up to four batteries of launchers. Each DDU has a 9S457M command post (CP) that receives information from external sources via the Polyana-D4M1 system, a 9S15M ‘Bill Board' all-round surveillance radar, and a 9S19M Imbir ‘High Screen' sector surveillance radar. Each battery includes a 9S32M ‘Grill Screen' multichannel missile guidance radar (MMGR), and 9A82 transporter/erector/launcher and radar (TELAR) each with four 9M83M-1 missiles and/or 9A83 TELARs with two 9M82M-1 missiles in transport-launch containers (TLC).
S-300V4部署在营级,由一个目标探测和指定单元(DDU)和最多四组发射器组成。每个DDU都有一个9S457M指挥所(CP),通过Polyana-D4M1系统接收来自外部来源的信息,一个9S15M”广告牌“(Bill Board)全方位监视雷达和一个9S19M Imbir“高屏幕”扇区监视雷达。每个连包括一个9S32M“格栅屏”多通道导弹制导雷达(MMGR)和9A82运输/起竖/发射运输车和雷达(TELAR),每个都带有四枚9M83M-1导弹和/或9A83远程雷达连同两枚装在贮运发射箱(TLC)中的9M82M-1导弹。
Continuous-wave (CW) illuminators are included with the 9A82 TELAR on a steerable high-gain antenna that is mounted on the front of the vehicle roof, which is used to transmit mid-course guidance commands to the missile.
9A82”运输-起竖-发射-雷达车“(TELAR)配备了连续波(CW)照射器,该照射器安装在车顶前部的可操纵高增益天线上,用于向导弹发送中途制导命令。
The system has a maximum interception range of 400 km against targets at an altitude of up to 40 km. Once the missiles are fired, the TELAR works with the battery's ‘Grill Screen' radar by ‘gathering' the missile in its radar beam and transmitting the necessary guidance course correction signals to intercept the target. When operating under conditions of active jamming, the ‘co-ordinate support' mode is used, whereby the range to the target is determined using the target detection radars (9S15M Obzor-3 and 9S19M Imbir), and its angular co-ordinates by the 9S32M ‘Grill Screen' missile guidance radar. This focuses a high amount of radio frequency (RF) energy from different sources for continuous wave illumination to the 9M82/9M83 missiles' semi-active radar seekers during the terminal guidance phase of the engagement.
该系统对高度高达40公里的目标的最大拦截距离为400公里。一旦导弹发射,远程雷达与连队的“格栅屏”雷达协同工作,通过在其雷达波束中“收集”导弹,并发送必要的制导航向修正信号来拦截目标。在有源干扰条件下工作时,使用“坐标支持”模式,通过目标探测雷达(9S15M Obzor-3和9S19M Imbir)确定目标距离,并通过9S32M“格栅屏”导弹制导雷达确定其角度坐标。在交战的末制导阶段,它将来自不同来源的大量射频(RF)能量集中到9M82/9M83导弹的半主动雷达导引头上,用于连续波照射。
While open-source intelligence (OSINT) has identified the deployment of the S-300V4, the veracity of this information can be difficult to confirm because of the availability of highly realistic decoys based on obsolete PT-76 tanks. The LPPU-83 (Lozhnaya Podvizhnaya Puskovaya Ustanovka – Self-Propelled Launcher Decoy) mimics the 9A83 (9A83-1) TELAR vehicles used by the S-300V, but utilises the PT-76 light-tank chassis rather than the real vehicle's tracked platform.
虽然开源情报(OSINT)已经确定了S-300V4的部署,但由于基于过时的PT-76坦克的高度逼真的诱饵的可用性,这一信息的准确性可能很难确认。LPPU-83(Lozhnaya Podvizhnaya Puskovaya Ustanovka——自行式发射器诱饵)模仿S-300V使用的9A83(9A83-1)远程车辆,但使用PT-76轻型坦克底盘,而不是真正车辆的履带平台。
The 9A83, a modern derivative of the full-tracked MT-T tractor chassis (originally designed and built at the Kharkov Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau in Ukraine), has seven road wheels per side while the PT-76 has only six per side. However, the rebuild to the LPPU-83 configuration stretches the chassis, adds a seventh roadwheel, and fits a 9A83-style crew cabin. Since it is powered by a diesel engine, it will have a suitable thermal signature, but it is not known whether the simulated tracking radar can emit the appropriate RF signature.
9A83是全履带MT-T拖拉机底盘(最初由乌克兰哈尔科夫·莫罗佐夫机械制造设计局设计和制造)的现代衍生车型,每侧有七个车轮,而PT-76每侧只有六个车轮。然而,对LPPU-83配置的改造延伸了底盘,增加了第七个车轮,并适合9A83风格的乘员舱。由于它是由柴油发动机驱动的,因此它将具有合适的热特征,但不知道模拟跟踪雷达是否能发出合适的射频特征。
At the medium-SAM range of up to 100 km, the SA-11 ‘Gadfly'/ SA-17 ‘Grizzly' 9K317 Buk-M2/M3 can defend against unmanned aircraft, supersonic cruise missiles, aircraft, and short-range or theatre ballistic missiles (TBMs) at ranges from 3 km to 70 km and altitudes between 5 m to 35 km, with target speeds of up to 3 km/s. The vehicle takes five minutes to switch between road march state to its ready state, and is capable of repositioning in its ready state, but requires 20 seconds to return to full readiness after repositioning. A brigade capability would be controlled by one Polyana-D4M1 vehicle with four divizions, with each divizion fire unit consisting of one 9S18 Kupol search radar, one 9S510 vehicle, and three SAM batteries. A typical Buk battery will feature 2-3 TELAR vehicles, with each having its own 9S36 fire-control and missile guidance radar, four ready-to-launch missiles, one 9A36 target illumination radar, and two 9A316 transloader vehicles that are also capable of firing four missiles. Each 9S36 fire-control radar is capable of tracking 10 targets and illuminating four targets simultaneously, while the Buk-M3's 9A36 radar can track 10 and engage six targets at a distance of up to 120 km. The Buk-M3's 9M317M missile has active radar homing, while earlier missiles had SARH guidance. Each Buk-M3 TELAR can carry up to six missiles in canisters.
SA-11“牛虻”和SA-17“灰熊”9K317 Buk-M2/M3在最大100公里的中程防空导弹(SAM)射程内,可以在3公里到70公里的射程和5米到35公里的高度上防御无人驾驶飞机、超音速巡航导弹、飞机和短程或战区弹道导弹(TBM),目标速度高达3公里/秒。车辆需要5分钟才能从行进状态切换到就绪状态,并且能够在就绪状态下重新定位,但重新定位后需要20秒才能恢复到完全就绪状态。一个旅的能力将由四个分区连同一辆Polyana-D4M1车辆控制,每个分区的火力单元由一个9S18 Kupol搜索雷达、一辆9S510车辆和三个防空导弹连组成。一个典型的“山毛榉”连将配备2-3辆TELAR车辆,每辆车都有自己的9S36火控和导弹制导雷达、四枚准备发射的导弹、一个9A36目标照明雷达,以及两辆9A316转运车,它们也能发射四枚导弹。每个9S36火控雷达能够同时跟踪10个目标和照射4个目标,而Buk-M3的9A36雷达可以在120公里的距离内跟踪10个目标和攻击6个目标。Buk-M3的9M317M导弹具有主动雷达寻的功能,而早期的导弹具有SARH制导。每个Buk-M3 TELAR最多可携带六枚装在贮运发射箱中的导弹。
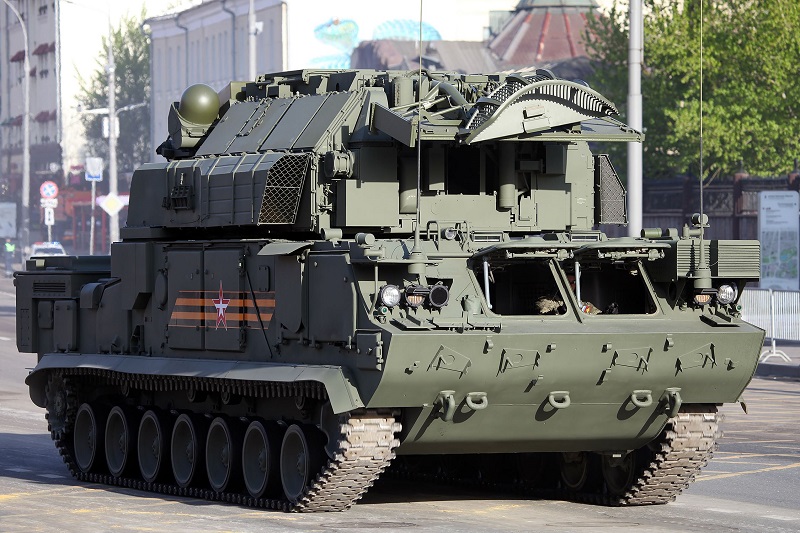

9K331“道尔”-M2
At the lowest level the 9K331 Tor-M2 is designed for engaging aircraft, cruise missiles, and unmanned platforms. It carries 16 ready-to-launch 9M338K missiles (earlier versions carry eight 9M331 missiles in canisters). It is capable of engaging four air targets simultaneously with a fire interval of two seconds, the system can engage targets at a range of 1.5–16 km and altitudes from 10 m to 12 km. It also has a launch on the move capability that supports missile firing when travelling at up to 40 km/h. Two Tor systems can be networked and can exchange information via radio datalink, and may be positioned at a maximum of 5 km from one another.
在最底层,9K331“道尔”-M2设计用于攻击飞机、巡航导弹和无人平台。它携带16枚可随时发射的9M338K导弹(早期版本携带8枚装在贮运发射箱中的9M331导弹)。它能够以两秒的射击间隔同时打击四个空中目标,该系统可以打击射程为1.5-16公里、高度为10米到12公里的目标。它还具有移动发射能力,在以高达40 公里/小时的速度行进时支持导弹发射。两个“道尔”系统可以联网,并可以通过无线电数据链路交换信息,彼此之间的距离最大为5公里。
A single 9S932-1 MRU-B vehicle equipped with the 1L122-1 radar – as part of the 9S931 Barnaul-T tactical level subsystem – can communicate with up to two higher-level control modules (9S931-1 or 9S931) and up to six lower-level modules (9S933 or 9S935), as well as Tor air-defence systems, and standalone radar systems. Target allocation commands are sent to lower-level units, while combat activity reports are passed to higher levels, with the system handling up to 100 targets. The 1L122 radar is also fitted with the Barrier-E bistatic system for the detection of low-flying targets and can acquire and maintain up to 30.
配备1L122-1雷达的单个9S932-1 MRU-B车辆(作为9S931 Barnaul-T战术级子系统的一部分)可以与多达两个更高级别的控制模块(9S931-1 或9S931)和多达六个较低级别的模块(9S933或9S935),以及“道尔”防空系统和独立雷达系统。目标分配命令下发给下级单位,而战斗活动报告则发送给上级单位,系统最多可处理100个目标。1L122雷达还配备了Barrier-E双基地系统,用于探测低空飞行目标,最多可以捕获和跟踪30个目标。
上一篇:Air Defense: S-350 SAM (Surface to Air Missile), S-400 Budget Version 下一篇:没有了
| Hammer and shield: Russia's modernised radar and early warning systems
锤子和盾牌:俄罗斯的现代化雷达和预警系统 |
| Russian ABM radar coverage from long-range systems is shown in this screenshot from a news article on the main missile warning centre in Moscow posted by the Russian Ministry of Defence on 16 February 2022. ... [2022-03-12] |
| Air Defense: S-350 SAM (Surface to Air Missile), S-400 Budget Version
防空:俄罗斯S-350防空导弹系统,S-400廉价版本 |
| The S-350 is, in effect, “S-400 Lite”. In other words a less expensive SAM system with many S-400 capabilities but not the billion dollar per battery price.... [2020-04-05] |
