| Shafrir 1
以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir) 1空对空导弹 Date:2016-03-30 Source:israeli-weapons By:Globalmil Viewed: |
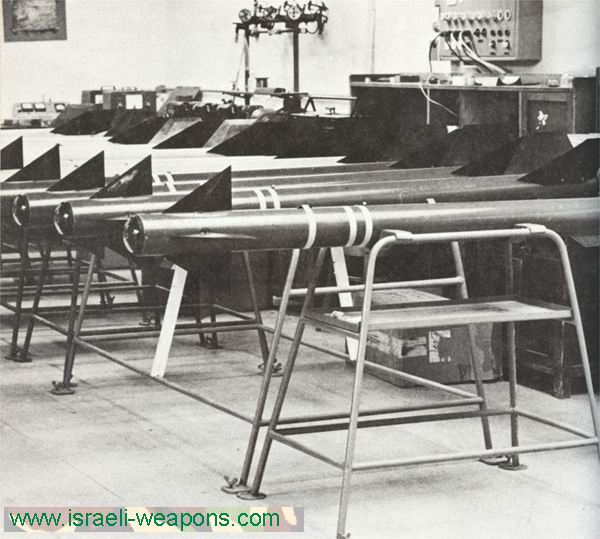

生产中的以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1 空对空导弹
Air to air missile projects have started to occupy the IAF from the late 1950's. In 1959 Israel began to develop the Shafrir 1 air to air missile. Five years later in July 1964 the development was completed.
以色列空军(IAF)从1950年后期启动空对空导弹计划。在1959年以色列开始发展“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1 空对空导弹。经历五年之后在1964年7月发展完成。
In March 1961 it was revealed that basic assumptions related to the missile's design were wrong. Before ending the development or conducting launch testing of the missile, engineers at Rafael had already started to think about ways to improve the missile's performance envelope.
在1961年3月显示涉及导弹的设计的基本设想是错误的。在结束发展或引导开始导弹测试之前,在以色列拉菲尔武器发展局(Rafael)设计已经启动想方法改进导弹的性能包线。
These improvements included an offer to enlarge its dimensions diameter would be increased from 11cm to 14cm, length from 2m to 2.5m, weight from 30kg to 65kg, and the explosive material from 11kg to 30kg.
这些改进包括要增大它的直径尺寸的提议,将会增加从11厘米到14厘米;长度从2米到2.5米;重量从30公斤到65公斤和装药从11公斤到30公斤。
The designers at Rafael pointed out that these changes in the missile would enable them to use a larger rocket motor, thus increasing the missile's effective hit range from 1.5km to 3km at low altitude, and from 3km to 9km at 35,000ft.
以色列拉菲尔武器发展局(Rafael)的设计者指出这些方面的改变导弹会能够使用一部较大的火箭发动机,如此增加导弹的有效攻击射程,在低高度从1.5公里到3公里和在35,000英尺从3公里到9公里。

以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1 空对空导弹在场地测试
Despite the fact that the designers were not satisfied with the basic design of the missile, a decision to equip the air force with 200 missiles was made.
尽管设计者没有对导弹的基本设计感到满意,要采用200枚导弹装备空军的一个决定被作出。
The fear that improvement works would extend the development process and cause a delay in the missile's operational deployment was the main reason to reject these offers. Nevertheless, during 1962 some design works were done at Rafael to improve the existing model, but never came into realization .
担心改进工程将延长开发过程和导致导弹操作部署延误是拒绝这些提议的主要理由。然而,在1962年一些设计工作在以色列拉菲尔武器发展局(Rafael)被做去改进现有型号,但是从未进入实现。
In March 1963, the Shafrir 1 was ready to be tested for the first time. The testing took part in France , and the missile was about to show its ability in shooting a maneuvering target. The result was quite of a disappointment. This led to the recognition that the Shafrir 1 would not be able to answer the IAF's operational requirements. Considering the fact that no other substitute was available, it had been decided that the Shafrir 1 would be received in the air force in May 1963. In parallel, the improved missile's program would be completed and the improvements would be put into the missile.
在1963年3月,“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1准备好第一次测试。测试支持在法国,而且导弹射击一个机动目标去显示它的能力,结果相当失望。这导致承认“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1不能够响应以色列空军(IAF)的操作需求。考虑事实上没有其它的可得的替代者,它已经被确定“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1会在1963年5月被空军接收到。并行地,改进导弹计划会被完成而且改进将进入导弹之内。

测试发射“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1导弹
Another issue which was discussed during the development process was the missile's proximity fuse. The fuse was based on a blast explosive, and was only efficient for about one meter from the target, so it was agreed that the explosive would be based on fragments. An option of increasing the warhead in price of performance decrease was considered also.
在发展过程期间另外讨论的问题是导弹的近炸引信。引信以一个爆炸炸药为基础,而且仅仅距离目标一米有效,因此一般赞同炸药会以破片为基础。增加性能减少价格弹头的选择项也被考虑。
The testing in France had showed its sign in the Shafrir 1 operational manual which saw light on July 18 th 1963 , during the missile's reception in the Mirage C3 (Shahak) squadrons
• Shooting would be done only on a non maneuvering target.
• Launching would be done on a traverse angle of +10/ 10 degrees of the target's flight line.
法国的测试已经显示它签收了“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1的操作说明书停落于1963年7月18日,在幻影C3(Shahak)空军中队导弹接收期间。
• 射击会仅仅在非机动目标上做。
• 发射会在目标飞行路线+10/10度的一个导向角去做。
Shafrir 1 performance was worse then its characterization had suggested. The missile's destroy rates were estimated at 21 percent without proximity fuse and 47 percent with the fuse.
“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1性能很差因而它的品质鉴定已经提出。导弹的杀伤率被估计没有近炸引信在21%和采用引信在47%。
It was cleared then, that a new air to air missile was needed to be developed. In May 1964, one year after being operational, it was agreed that the Shafrir 1 missile had not passed the reception test.
它然后被清除,需要去发展一个新的空对空导弹。在1964年5月,这是在操作之后一年,它确认了“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1导弹没有通过验收试验。
The Shafrir 1 was not satisfying as a weapon system, but had its credit for laying the foundations for the successful next generations of Israeli air to air missiles Shafrir 2.
“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1被当做一种武器系统不是令人满意,但是为成功的下一代以色列的空对空导弹“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)2铺设基础有它的声望。
|
长度(Length)
|
250 cm
|
|
翼展(Span)
|
55 cm
|
|
弹体(Body)
|
15 cm
|
|
重量(Weight)
|
93 kg
|
|
制导类型(Guidance Type)
|
IR
|
|
类型(Model)
|
1 x spr.
|
|
射程(Range)
|
5 km
|
上一篇:没有了 下一篇:Shafrir 2
| Python 4:A Leader in Short Range Air-to-Air Weapon Systems
以色列“蟒蛇”(Python) 4:一个短距空对空武器系统的领导者 |
| The Python 4 fourth generation Air-toAir missile, in operational use in the Israeli Air Force , features a novel "no escape volume" performance with a unique aerodynamic configuration for superior agility.... [2016-04-07] |
| Python 3
以色列“蟒蛇”(Python)3近距空对空导弹 |
| Python 3 is a third generation short to medium range air-to-air missile adapted to the F-15, F-16, all types of Mirage, F-5, F-4 and Kfir C-2 and C-7 aircraft.... [2016-03-30] |
| Shafrir 2
以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)2格斗导弹 |
| The Shafrir 2 answered the engineer's expectations. It withstood almost all the designing demands they had faced it with.... [2016-03-30] |
| Shafrir 1
以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir) 1空对空导弹 |
| Air to air missile projects have started to occupy the IAF from the late 1950's. In 1959 Israel began to develop the Shafrir 1 air to air missile.... [2016-03-30] |
