| Python 4:A Leader in Short Range Air-to-Air Weapon Systems
以色列“蟒蛇”(Python) 4:一个短距空对空武器系统的领导者 Date:2016-04-07 Source:israeli-weapons By:Globalmil Viewed: |
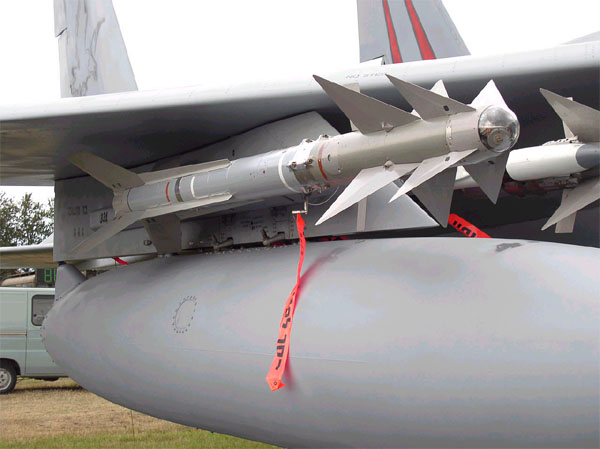

The Python 4 fourth generation Air-toAir missile, in operational use in the Israeli Air Force , features a novel "no escape volume" performance with a unique aerodynamic configuration for superior agility. The state-of-the-art, high performance seeker incorporates an advanced IRCM & background rejection capabilities. The missile includes a highly effective fragmentation warhead. Python 4 is a very nimble "fire and forget" missile with an improved maneuvering capability. It has an advanced homing head with a lateral "squint" capability which allows it to receive signals from the line of vision of the pilot who sees the enemy plane through a special (Elbit-developed) helmet. The missile receives these signals and hits the enemy plane without requiring the pilot to steer his aircraft at the enemy plane. The Python 4 can be launched at a range of over 15 km, its warhead is over 11 kg, and its electromagnetic proximity fuze is one of the best in the world.
“蟒蛇”(Python)4第四代空对空导弹,在以色列空军操作使用中,特点是一种新的“不能逃避量”性能采用一种独特的空气动力学结构用于优越的敏捷性。最新颖的,高性能自动导引头整合一个先进的红外对抗(IRCM)&背景抑制能力。导弹包括一个高有效破片弹头。“蟒蛇”(Python)4是一种非常敏捷的“射后不理”导弹具有改进的机动能力。它具有先进的寻的头横向“斜视”的能力,使其从飞行员的视觉看到敌机通过特殊(Elbit-发展)头盔线接收信号。导弹接收到这些信号,并击中敌人的飞机,而不需要飞行员驾驶他的飞机向着敌人的飞机。Python 4的射程能够超过15公里,弹头超过11公斤,其电磁近炸引信是世界上最好的之一。
The Indian Air Force has reportedly purchased the Python 4 air-to-air missile. The missile, produced by Rafael, is considered one of the most advanced short distance missiles in the world.
印度空军已经根据传闻购买“蟒蛇”(Python)4空对空导弹。被以色列拉菲尔武器发展局(Rafael)生产的导弹,被考虑是世界上最先进的短距导弹之一。
Israel has had the unenviable experience of being surrounded by much larger neighbours most of whom, since 1948, have had an openly declared intention to destroy the Jewish state. Since 1948, the Israelis have fought a number of wars in order to initially survive, and later to secure their borders. In every single instance, air superiority proved to be the decisive factor in achieving both tactical and strategic victories on the battlefield. Current Israeli military doctrine accords the maintenance of air superiority the highest priority.
以色列已有尴尬经历被大得多的邻居包围大部分人,自从1948年以后,有一个公开宣称的意图摧毁这个犹太国家。自从1948年以后,以色列人打了许多的战争为了要最初生存和稍后巩固他们的边境。在每一个单独的实例中,空中优势被证明是在完成战场上的战术和战略胜利方面的决定性因素。目前以色列的军事教条一致维持空中优势最高的优先权。
One of the consequences of Israel's military experience since the sixties has been to develop a strong domestic capability to design and manufacture modern military equipment and weapons. Indeed their experience in the sixties, when France unilaterally withdrew all support for French equipment in Israeli service, and more recently US dithering over the supply of aircraft has led the Israelis to source as many "consumables" as possible from domestic manufacture. Since the WVR AAM is such a critical component of the air superiority game, the Israelis have been building their own since the early sixties.
以色列军事经验的一个后果是从1960年后发展一个强大的国家能力去设计和制造现代化的军事装备和武器。的确他们在1960年的经验,当法国在那时候对以色列服役的法国装备单方面撤回了所有的支援,而且最近美国在飞机的供给上迟疑已经致使以色列尽可能从国内制造许多的“消耗品”。由于视距内(WVR)空对空导弹(AAM)是空中优势比赛的一个具决定性的组成物,以色列已经从1960年自己制造。
The first Israeli AAM to see production was the Rafael Shafrir (Dragonfly) I in the early sixties, a contemporary of the AIM-9B. It was followed by the improved Shafrir II, in production between 1968 and 1980 and credited with over 100 kills, mainly during the 1973 Yom Kippur war. The third generation Python 3, a contemporary of the AIM-9L/M, was introduced during the late seventies and is credited with over 35 Syrian aircraft kills during the Bekaa Valley air battle in 1982. Both the Shafrir and the Python 3 utilise a similar aerodynamic and control configuration to the AIM-9, but are unique missile designs.
去了解以色列生产的第一种空对空导弹(AAM)是早在60年代色列拉菲尔武器发展局(Rafael)的“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)1,AIM-9B的一个同时代产品。它被改进“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)2后继,生产在1968年和1980年之间而且记录超过100个杀伤,主要在1973年赎罪日战争期间。第三代“蟒蛇”(Python)3,AIM-9L/M的一个同时代产品,引进在七十年代晚期而且在1982年贝卡(Bekaa)谷空战期间记录摧毁超过35架叙利亚飞机。“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)和“蟒蛇”(Python)3都采用一个类似ATM-9的气体力学和控制结构,但是独特的导弹设计。
The fourth generation Python 4 was developed during the late eighties and early nineties, deploying on Israeli F-15 and F-16 fighters during the early nineties. The missile and its associated Elbit DASH (Display And Sight Helmet) third generation HMS were developed specifically to outperform the Soviet Archer/HMS and MiG-29, both of which deployed in the Middle East by the early nineties.
第四代“蟒蛇”(Python)4在八十年代晚期和九十年代早期发展,九十年代早期在以色列F-15和F-16战斗机上配置。导弹和它联接的埃尔比特(Elbit)DASH (显示和瞄准头盔)第三代头盔瞄准具(HMS)的发展明确地超过苏联射手/HMS和米格-29,两者在九十年代早期在中东部署。
The Python 4 is a true fourth generation missile, designed from the ground up for the demanding requirements of this style of air combat. It employs an all aspect gimballed seeker designed for large off boresight acquisition and tracking angles, and a high tracking rate. It also employs a new powerplant, and unique aerodynamics specifically optimised for high agility.
“蟒蛇”(Python)4是真正的第四代导弹,设计从地面上为空战的类型的苛刻的需求。它采用一个全方位万向架导引头设计用于大离瞄准线捕获和跟踪角,还有一个高跟踪速度。它也采用一个新的动力装置和独特的空气动力学设计为高敏捷性特别优化。
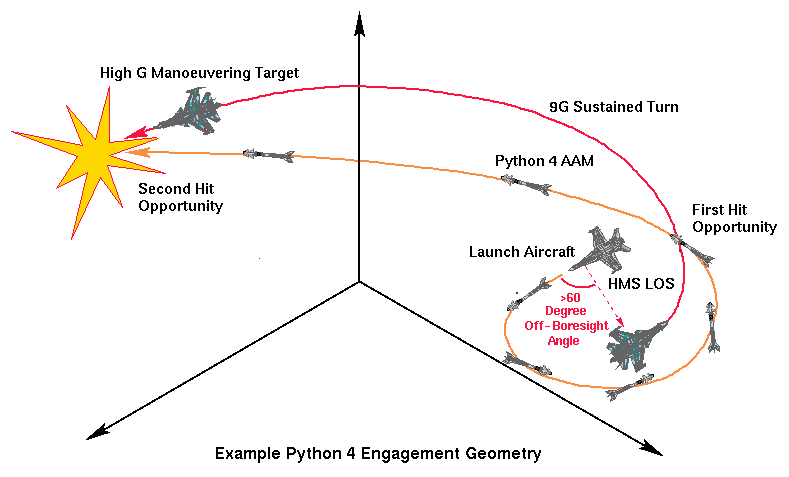
The intent of the designers was to produce a missile which can not only be shot from a wider range of angles than earlier missiles, but which can also maintain track on a highly manoeuvrable high G target engaged during the merge or opening phase of an engagement. A passing target on a reciprocal heading can be engaged in most of the forward hemisphere, if the Python fails its first opportunity to hit, it will maintain track on the target and continue a tail chase geometry pursuit on a reciprocal heading to the launch aircraft, running down the target for a tail-aspect hit. The missile is claimed to have sufficient turning performance to defeat high G evasive manoeuvre by any existing fighter aircraft. Existing ACM experience with the missile suggests a typical engagement duration of much less than 30 seconds.
设计者的意图要生产一种导弹能够不但从超过早期导弹的宽范围角发射,而且在一次交战的交汇或开场阶段期间也能对高机动高G交战目标保持跟踪。相向而过的目标能够在大多前半球交战,如果“蟒蛇”(Python)第一次打击机会失败,它将会保持在目标上跟踪而且在对飞机发射的相反方向连续尾部寻觅几何跟踪,碰撞目标用于尾-方位打击。导弹被宣称足够去击败任何现有战斗机的高G逃避机动。已有的空战(ACM)在导弹使用方面的经验认为一个典型的交战期间大多少于30秒。
This capability was achieved by carefully optimising seeker, aerodynamic and powerplant performance.
这种能力实现是通过仔细优化导引头,空气动力学和动力性能。
The seeker was incorrectly reported by US sources to be a cooled two colour rotating reticle design, Israeli sources will only acknowledge that the missile usesa multiple detector array seeker, which has an IRCCM (ie IR ECCM) capability and the ability to reject background IR radiation. Typical two colour seekers (eg FIM-92C Stinger) use an Argon cooled InSb 4 micron IR detector and a Si or GaAs UV detector. Valid aircraft targets have a low UV signature and a high IR signature and this enables the Stinger to easily reject spurious targets such as flares. The Python 4 seeker has been credited with significantly better acquisition range than that of the AIM-9M, which is consistent with the sensitivity improvement produced by a multiple element seeker.
导引头被美国来源错误的报告是一种冷凝双色的旋转瞄准线设计,以色列方面的消息只会承认导弹使用多重探测阵列导引头,具有抗红外干扰(即IR ECCM)能力和抑制背景红外辐射的能力。典型的双色跟踪头(如FIM-92C Stinger)使用氩气冷却的InSb 4微米的红外探测器和Si或GaAs基紫外探测器。有效的目标有一个低紫外线特征和高红外特征,这使得毒刺容易拒绝虚假的目标如耀斑。Python 4导引头具有比AIM-9M更好的探测范围,这是一致的采用一个多元件导引头产生了灵敏度提高。

The Python 4 is known to employ digital signal processing techniques in the seeker, as well as a microprocessor based digital flight control system. The use of DSP (Digital Signal Processing) techniques will provide the seeker with better acquisition range than analogue seekers by exploiting the multiple detector elements to full advantage, as well as providing further IRCCM capability and the ability to intelligently manage fluctuating target signatures. A digital flight control system will allow the missile to optimise its flight control laws for the regime of flight, while also selectively choosing the most suitable homing algorithm parameters for the geometry of the engagement. The Python 4 missile employs a unique tailored proportional navigation homing algorithm. As a result of these design features, the Python 4 seeker is credited with the capability to engage and track targets throughout most of the forward hemisphere (the exact figure has not been disclosed, UK sources suggest in excess of 60 degrees off-boresight capability), with a high but undisclosed tracking rate.
Python 4已知导引头使用数字信号处理技术,以及一个基于微处理器的数字飞行控制系统。使用DSP(数字信号处理)技术将导引头运用多重检测器元件的充分优势提供比模拟导引头更好的探测范围,以及提供进一步的抗红外干扰( IRCCM)能力和智能应付目标特征波动的能力。数字飞行控制系统将允许导弹优化其飞行控制规则用于飞行管控,同时对目标的几何现状也选择性的选择最合适的自动导引算法参数。Python 4导弹采用一个独特的量身定制的比例导引制导算法。由于这些设计特点,Python 4导引头有能力在大部分的前半球来交战和跟踪目标(确切数字尚未公布,英国消息表明超过60度的离轴能力),具有高但未公开的跟踪速率。
The missile employs a blast fragmentation warhead which is triggered by an active laser proximity fuse with a backup impact fuse, a design feature in common in the AIM-9, but different from the Archer which employs a radio proximity fuse. The warhead size has not been disclosed.
导弹采用爆炸破片式战斗部被主动激光近炸引信连同备份碰撞引信引发,同AIM-9共同的设计特点,但不同的是“弓箭手”(Archer)采用无线电近炸引信。弹头尺寸尚未披露。
The Python 4 employs a 6 in diameter rocket motor, a feature it shares with the Archer and the ASRAAM. The long burn motor has a tailored thrust profile to achieve optimal acceleration for close-in closing engagements and high energy for terminal phase homing or end-game engagement. Thrust vectoring is not employed, the missile instead utilises aerodynamic design to achieve a high turn rate throughout the its flight envelope.
Python 4采用6英寸直径火箭发动机,它与“弓箭手”(Archer)和先进短程空对空导弹( ASRAAM)共同特征。长燃烧发动机具有量身定制的推力曲线,以达到优化加速用于接近关闭发动机和高能量用于末端引导或交战结束。没有采用推力矢量,导弹反而利用空气动力学设计实现整个飞行包线的高转化率。
The aerodynamic design of the Python is by any standard the most complex in any existing AAM, and is evidently intended to provide the best possible lift throughout the flight profile of the weapon. A cruciform fixed canard is mounted on the nose to stabilise high angle of attack airflow over the cruciform canard control surfaces, which are used for pitch and yaw control, a technique used by a number of existing WVR AAMs. Roll control is achieved by a small pair of "paddle" vanes aft of the controls. The missile employs highly swept strakes along the fuselage which are intended to improve airflow characteristics over the tail surfaces. The swept tail surfaces are designed to swivel about the fuselage, this is designed to minimise lift induced rolling moments at high angles of attack in high G turns.
Python的空气动设计以任何标准在任何现有的空空导弹中最复杂的,显然是为了在武器整个飞行轨迹中提供最好的尽可能的升力。十字形固定鸭翼安装在弹鼻上稳定高攻击角在十字形鸭式控制面上气流,用于俯仰和偏航控制,使用一些现有视距内(WVR)空空导弹的技术。侧滚控制是使用一对小“桨”尾部叶片控制。导弹采用沿机身后掠边条的目的是改善尾部表面气流特性。后掠尾翼设计为左右旋转机身,这是为了尽量减少升力在高G转弯大迎角攻击时产生侧转力矩。
The combination of a long burn motor and complex aerodynamic design will provide the Python 4 with a high sustained turn rate at all speeds, and this will in turn translate into an ability to follow a high G target throughout any manoeuvre. The missile is credited with much better range performance than the AIM-9M, and better maximum G capability than any existing AAM.
长时间燃烧发动机和复杂气动设计的组合将提供Python 4在所有的速度高持续转弯率,这将转化成一种能力,在任何技术动作下追随高G目标。导弹归功于更好的射程性能超过AIM-9M,和更好最大G能力超过任何现有的空空导弹。
The Python 4 is compatible with all standard AIM-9 capable launchers, and has been tested and cleared for use on the F-15, F-16, F/A-18 and F-5. The only integration requirement for the basic missile is the replacement of the launcher internal electronic unit with a Python capable design, which retains compatibility with the AIM-9. To fully exploit the missile's capability, a Helmet Mounted Sight is required, which will necessitate the fitting of cockpit transducers and supporting electronics. The DASH HMS supports either an analogue or digital interface. Aircraft such as the F/A-18 will also require some changes to the fire control software, to enable selection of the HMS or radar for missile boresight control. The F/A-18 could carry up to six rounds on wingtip and pylon stations.
Python 4是兼容所有标准AIM-9发射器,已经过测试,并允许F-15、F-16、F/A-18和F-5 F使用。唯一的整合要求基本导弹是Python能够设计,以保持与AIM-9发射器内部电子部件的更换兼容性。要充分利用导弹的能力,需要头盔瞄准,这将有必要的驾驶舱传感器和配套电子配件。DASH HMS支持模拟或数字接口。如F/A-18飞机还将要求火控软件的一些变化,为了去选择头盔瞄准具(HMS)或雷达导弹瞄准控制。F/A-18在翼尖和外挂点最多携带六枚。
The Python 4 is currently being bid for the AIR 5400 requirement, and the RAAF have acknowledged that captive carry tests were flown by ARDU late last year. No further details have been disclosed at this time.
Python的4目前正在为AIR5400要求投标,澳大利亚皇家空军承认,性能进行测试由ARDU去年年底飞行。没有进一步的细节在这个时候公开。

Main Features
主要特点
A fully developed fourth generation missile, tested and proven in the western world
Superior "agile" aerodynamic configuration optimized for within visual range dogfights
Radically expands the "no escape zone" up to most of the frontal hemisphere
Increased range and kinematic performance
Unique pursuit trajectories; advanced IRCCM capability
一个全面发展的第四代导弹,在西方世界测试和证明
先进的“敏捷”气动外形优化视距内空战
从根本上扩展了“无法逃逸区”做到大部分的前半球
增加射程和运动学性能
独特的追赶轨迹;先进的抗红外干扰能力
|
Length(长度)
|
295 cm
|
|
Span(翼展)
|
50 cm
|
|
Body(弹体)
|
15 cm
|
|
Weight(重量)
|
120 kg (warhead over 11 kg)
|
|
Guidance Type(制导类型)
|
IR
|
|
Model(模式)
|
1 x spr.
|
|
Range(射程)
|
15 km
|
上一篇:Python 3 下一篇:没有了
| Python 4:A Leader in Short Range Air-to-Air Weapon Systems
以色列“蟒蛇”(Python) 4:一个短距空对空武器系统的领导者 |
| The Python 4 fourth generation Air-toAir missile, in operational use in the Israeli Air Force , features a novel "no escape volume" performance with a unique aerodynamic configuration for superior agility.... [2016-04-07] |
| Python 3
以色列“蟒蛇”(Python)3近距空对空导弹 |
| Python 3 is a third generation short to medium range air-to-air missile adapted to the F-15, F-16, all types of Mirage, F-5, F-4 and Kfir C-2 and C-7 aircraft.... [2016-03-30] |
| Shafrir 2
以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir)2格斗导弹 |
| The Shafrir 2 answered the engineer's expectations. It withstood almost all the designing demands they had faced it with.... [2016-03-30] |
| Shafrir 1
以色列“蜻蜓”(Shafrir) 1空对空导弹 |
| Air to air missile projects have started to occupy the IAF from the late 1950's. In 1959 Israel began to develop the Shafrir 1 air to air missile.... [2016-03-30] |
