| Brief History of PLA's Type 83 273mm Multiple Rocket Launcher System
中国83式273毫米多管火箭发射系统发展史 Date:2017-01-15 Source:Internet By:Globalmil Viewed: |

In the late 1950s, No.123 Manufacturing Plant began its own large caliber multiple rocket launcher (MRL) development. This project, like many other military projects was severely disrupted in the 1960s during the Cultural Revolution. It was not until 1978 that major development efforts resumed on the project. In 1984, the plant finally rolled out the 273mm caliber MRL and designated as the Type 83 273mm MRL.
在1950年后期,第123制造厂开始了它自己的大口径多管火箭发射装置(MRL)发展。这一个计划,像许多其它的军队计划,严重地在1960年的文化大革命期间被打乱。它直到1978年才在计划上恢复主要的发展工作。在1984年,制造厂大量生产出273毫米口径MRL,而且指定被称为83式273毫米MRL。
The launcher assembly carries 4 rockets, and is mounted on a Type 60 artillery tractor for mobility. The rockets are free-flight, spin-and-fin stabilized rockets, and do not have guidance systems. As a result, the Type 83’s accuracy especially in term of directional (azimuth) dispersion is much lower than other projectile weapon systems such as traditional tube artillery guns. Rocket system accuracy had always been a major weakness and technical bottleneck. Thus, this was the main area where the designers concentrated their development efforts.
发射装置装配携带4枚火箭,而且被安装在一辆60型火炮牵引车上用于机动。火箭是无控-飞行、旋转-和-翼稳定火箭,而且没有制导系统。结果,83式精度尤其在方向(方位)散布的项目上比其它的发射武器系统,像是传统的管式火炮更加低。火箭系统精度已经是一个主要的弱点和技术上的瓶颈。因此,这是设计者集中他们的发展努力的主要范围。

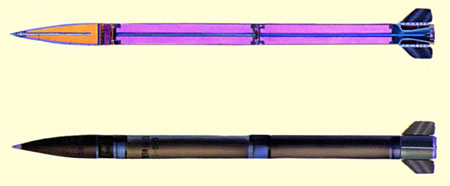
The rocket of the 273mm MRL has a range of 40km with a 138kg warhead. In pursuing specifications set out for the system, the designers had adopted a series of rocket design features. These features included:
273毫米MRL的火箭有一枚138公斤弹头,射程40公里。为推行规范测定用于系统,设计者已经采用一系列的火箭设计特点。这些特点包括:
Attempts at controlling the rocket's rotation velocity and its directional state at the precise moment departs from launch rail;
Anhancement of the rocket body's mechanical precision characteristics through better quality manufacturing process;
Improvement of its internal ballistic performance.
·尝试在火箭的旋转速度控制和它的方向状态,从发射轨道上瞬间精确离开;
·经过更好质量的制造过程完成火箭弹体机械精度性状;
·改进它的内部弹道性能。
As for the launch platform, improvements were made to its structural design. These included reinforcing the launcher structural members to increase rigidity, and reducing launcher interference with the rocket body's initial flight. However, despite all these measures the overall system performance was not satisfactory with regard to accuracy, and in tests did not demonstrate an acceptable level of performance.
至于发射平台,从结构设计改进。这些包括加固发射结构的构件去增加刚性,而且减少发射装置与火箭弹体开始飞行的干扰。然而,尽管所有的这些措施总体系统性能考虑到精度不令人满意,而且在测试中没有证明一个可接受水平的性能。
·尝试在火箭的旋转速度控制和它的方向状态,从发射轨道上瞬间精确离开;
·经过更好质量的制造过程完成火箭弹体机械精度性状;
·改进它的内部弹道性能。
As for the launch platform, improvements were made to its structural design. These included reinforcing the launcher structural members to increase rigidity, and reducing launcher interference with the rocket body's initial flight. However, despite all these measures the overall system performance was not satisfactory with regard to accuracy, and in tests did not demonstrate an acceptable level of performance.
至于发射平台,从结构设计改进。这些包括加固发射结构的构件去增加刚性,而且减少发射装置与火箭弹体开始飞行的干扰。然而,尽管所有的这些措施总体系统性能考虑到精度不令人满意,而且在测试中没有证明一个可接受水平的性能。
Throughout various experiments on the system, the rocket's body exhibited signs of unstable flight and inconsistent dispersion. This made prediction of its flight path extreme difficult. In one trial test an accident occurred. A rocket had exploded within the launcher frame, causing all other rockets to explode simultaneously — An undocumented incident just short of a total disaster. This incident had a great impact on the system's development and nearly jeopardized the existence of the whole project. During the 1980s, military funding was so scarce that a single mishap could have proved one too many.
在系统上遍及各种不同的实验,火箭弹体显示不稳定的飞行迹象和不一致的散布,这使预测它的飞行路径末端是困难的。在一次探索性试验中一个事故发生。一枚火箭已经在发射装置框架内爆炸,引起所有的其它火箭同时地爆炸—在全部事故中仅仅一次未被记录的事故。这一个事件在系统的发展方面造成很大冲击和几乎危害了整个的计划存在。在1980年,军事资金非常缺少,以致于一次个别事故应该已经证明(该项计划)是多余的(不需要的)。
在系统上遍及各种不同的实验,火箭弹体显示不稳定的飞行迹象和不一致的散布,这使预测它的飞行路径末端是困难的。在一次探索性试验中一个事故发生。一枚火箭已经在发射装置框架内爆炸,引起所有的其它火箭同时地爆炸—在全部事故中仅仅一次未被记录的事故。这一个事件在系统的发展方面造成很大冲击和几乎危害了整个的计划存在。在1980年,军事资金非常缺少,以致于一次个别事故应该已经证明(该项计划)是多余的(不需要的)。
The 273mm system had to contend with an extended range 122mm 40 barrel MRL from No.5137 Manufacturing Plant. The improved 122mm system, which later become the Type 90 MRL, also has a 40km range and it was in early development during the same time. However, despite much debate, work did continue based on the argument that the PLA in need of large caliber rocket artillery system for fire support and to compensate the lack of short-range tactical ground-to-ground missiles. In addition, the 273mm rockets have much more growth potential for range, payload and warhead types than the smaller 122mm system.
273毫米系统必须同来自第5137制造厂增程122毫米40管MRL抗衡。改进的122毫米系统,稍后变成90式MRL,射程40公里,它是在相同的时间在早期发展中。然而,不管很多的辩论,工作确实继续基于PLA理论需要大口径火箭炮系统用于火力支援和补偿近程战术地对地导弹的缺乏。除此之外,273毫米火箭在射程、负载量和弹头类型有更多增长潜力胜于较小的122毫米系统。
273毫米系统必须同来自第5137制造厂增程122毫米40管MRL抗衡。改进的122毫米系统,稍后变成90式MRL,射程40公里,它是在相同的时间在早期发展中。然而,不管很多的辩论,工作确实继续基于PLA理论需要大口径火箭炮系统用于火力支援和补偿近程战术地对地导弹的缺乏。除此之外,273毫米火箭在射程、负载量和弹头类型有更多增长潜力胜于较小的122毫米系统。
Due to the non-satisfactory test results, a lengthy investigation identified two major problems with the system:
由于非-满意的测试结果,一个冗长的调查查明了系统二个主要的问题:
(a) Range accuracy Ex/x = 1/33.7 (2.9% of range) during high temperature environment of + 50° C is worse than at standard temperature. Not only so, it is much lower than that of low temperature at -40° C, where its accuracy is Ex/x = 1/83.8 (1.1% of range, nominal for fin-and-spin stabilized rockets). Such condition demonstrated unacceptable abnormality ballistic performance.
(a)射程精度Ex/x=1/33.7(2.9%的射程)在+50°C的高温度环境期间比较在标准的温度是更差的。不但如此,它与在-40°C低温度比较更低,它的精度是Ex/x=1/83.8的范围(1.1%的射程,标称用于翼-和-自旋稳定火箭)。如此的情形表明了无法接受的反常弹道性能。
(b) Data from a high-speed range camera in one of trail, shown the active flight phase of the four rockets, that is, an in-flight period when the main rocket is still functioning, the rockets from the most left and most right hand side of the launcher crossed each other’s path in-flight. Again, this is an unusual abnormality, and an indication of grossly unacceptable performance in azimuth dispersion.
(b)来自一部高速射程照相机的一个追踪数据,显示的四枚火箭的主动飞行阶段,也就是说,一个飞行周期内当主火箭一直运行的时候,火箭在发射装置侧面从最左和最右侧交叉各自的飞行路径。再一次,这是一个不寻常的反常,在方位散布性能上的非常无法接受的迹象。
The designers reckoned these two abnormalities should be treated together as one issue. Regarding the problems with low accuracy at high temperature and trajectory path crossing, investigation centered on the launcher rather than the rocket. They had discovered that, after the rocket's ignition, it completely left the launch rail and the stabilizer apparatus of the rectangular frame launcher had shown lateral vibration. This explained the path crossing of the rockets. And because vibration from the launch frame on both sides of the launcher was greater than those two in the middle, path crossing was more apparent. Later, researchers found out that movement of the stabilizer apparatus of the launcher was due to its frame structure design. During firing, gases from each launch frame producing a lateral force which then interacted with each adjoining structural components to rock the whole launch platform. This problem was exacerbated by gas pressure from the rocket's spin motor and main motor where their force vectors were in opposition. Further analysis also suggested this was also the cause for low accuracy under high temperature environments.
设计者处理这二次反常应该被一起对待当做一个议题。有关在高温低精度和弹道路径交叉问题,调查中心在发射装置上并非火箭。他们已经发现,在火箭点火之后,它完全地离开了发射轨道,而且矩形框架发射装置的稳定装置已经显示横向振动,这说明了火箭路径交叉。而且因为来自发射装置的发射框架两侧上振动更超过那二枚在中间的,路径交叉更明显。稍后,研究员发现发射装置的稳定装置的运动是由于它的框结构设计。在点火的时候,来自每个发射装置框架的气体产生一个横向力然后每个邻接的结构部件互动到整个火箭发射平台。这一个问题被来自火箭旋转稳定发动机和主发动机的气体加剧,在那里他们的力量矢量对抗。也进一步的分析也是在高温环境下的低精度因素。
设计者处理这二次反常应该被一起对待当做一个议题。有关在高温低精度和弹道路径交叉问题,调查中心在发射装置上并非火箭。他们已经发现,在火箭点火之后,它完全地离开了发射轨道,而且矩形框架发射装置的稳定装置已经显示横向振动,这说明了火箭路径交叉。而且因为来自发射装置的发射框架两侧上振动更超过那二枚在中间的,路径交叉更明显。稍后,研究员发现发射装置的稳定装置的运动是由于它的框结构设计。在点火的时候,来自每个发射装置框架的气体产生一个横向力然后每个邻接的结构部件互动到整个火箭发射平台。这一个问题被来自火箭旋转稳定发动机和主发动机的气体加剧,在那里他们的力量矢量对抗。也进一步的分析也是在高温环境下的低精度因素。
Based on analysis data modifications were drawn up to solve the problems. They included:
最后基于分析数据修改被列出去解决问题。它们包括:
最后基于分析数据修改被列出去解决问题。它们包括:
a) Redesign of the launcher from a exposed frame and rail to a enclosed case type design. This resulted in the dramatic reduction of lateral forces from rocket motor gases on lateral components of the launcher, and diverted the forces downward and away from the launcher.
b) Reduction of the spin motor apparatus's width, thus reducing torque from jetting gases;
c) Reducing the gap between the launcher casing and rocket body so vibration sources were minimized while the rocket being propelled out of the launcher and while still on the launch rail;
d) Improved quality control during manufacturing, which improved the launcher's vibration damping characteristics by increasing stiffness of the stabilizing apparatus and lateral locking system.
a)从一个外露的框架和轨道重新设计到一个封闭箱型设计。这导致显著减少来自火箭发动机气体在发射装置侧面部分的侧向力。而且将力向下转向和一直到离开发射装置。
b)减少旋转发动机装置的宽度,如此减少喷射气体扭矩;
c)减少发射装置箱和火箭弹体之间的间隙因此振动源被最小化,当火箭被推进从发射装置离开而且期间一直在发射轨道上;
d)在制造期间改进质量控制,被增加刚度的稳定装置和侧向锁紧装置改进发射装置振动衰减特性。
a)从一个外露的框架和轨道重新设计到一个封闭箱型设计。这导致显著减少来自火箭发动机气体在发射装置侧面部分的侧向力。而且将力向下转向和一直到离开发射装置。
b)减少旋转发动机装置的宽度,如此减少喷射气体扭矩;
c)减少发射装置箱和火箭弹体之间的间隙因此振动源被最小化,当火箭被推进从发射装置离开而且期间一直在发射轨道上;
d)在制造期间改进质量控制,被增加刚度的稳定装置和侧向锁紧装置改进发射装置振动衰减特性。
After these improvements the system finally achieved range dispersion of 1/134 (0.7%) and lateral dispersion of 1/83 (1.2%), performance as good as or better than other spin-and-fin stabilized rockets of the day. This then met the 'Combat Accuracy Criteria' for artillery weaponry set by the People’s Liberation Army.
在这些改进之后系统最后达到了1/134(0.7%)射程散布 和达到了1/83(1.2%)横向散布,性能优于当时其它的旋转-和-翼稳定火箭。这于是符合“战斗精度标准”(Combat Accuracy Criteria)用于人民解放军规定的火炮武器。
在这些改进之后系统最后达到了1/134(0.7%)射程散布 和达到了1/83(1.2%)横向散布,性能优于当时其它的旋转-和-翼稳定火箭。这于是符合“战斗精度标准”(Combat Accuracy Criteria)用于人民解放军规定的火炮武器。



The Type 83 MRL is currently in limited service with the PLA.
83式MRL目前在PLA的少量的服役中。
Although the Type 83 MRL experienced a long development and did not enter service in large numbers with the PLA, the project benefited No.123 manufacturing plant in that the staff accumulating much needed experience and data for later designs. And the decision to continue its development proved to be a right one. Succeeding the Type 83 is the Type WM-80, an eight-rocket launcher configuration mounted on a high mobility 8X8 truck. Due to the application of a high performance composite propellant the rocket is capable a range of exceeding 80km with a CEP of 800 meters or approximately 1% of the total range. In addition, the development of a simplified guidance system was mentioned in an early brochure of the WM-80.
虽然83式MRL经历了长时间发展而且没有大量进入PLA服役,但是计划使第123制造厂获益,全体人员累积了更多必需的经验和数据用于以后的设计。并且证明决定要继续发展它是正确的。83式随后的是WM-80式,一种八枚火箭的发射装置安装配置在一辆高机动8X8卡车。由于运用高性能复合推进剂,火箭增程到80公里具有800米或大约1%总射程的圆概率误差(CEP)。除此之外,简化制导系统的发展在WM-80的一本早期说明书中被提到。
虽然83式MRL经历了长时间发展而且没有大量进入PLA服役,但是计划使第123制造厂获益,全体人员累积了更多必需的经验和数据用于以后的设计。并且证明决定要继续发展它是正确的。83式随后的是WM-80式,一种八枚火箭的发射装置安装配置在一辆高机动8X8卡车。由于运用高性能复合推进剂,火箭增程到80公里具有800米或大约1%总射程的圆概率误差(CEP)。除此之外,简化制导系统的发展在WM-80的一本早期说明书中被提到。

The WM-80 rockets can be armed with a range of warheads. Its HE warhead has a blast radius of 70 meters and a single warhead can produce as many as 16800 fragments. The anti-tank cluster warhead has 380 bomblets that each can penetrate 80 to 100mm of top armor. In trials it proved to be a very effective weapon against armor columns and against armored personnel carriers in particular. Other warheads available include incendiary and an fuel-air explosive warhead which potentially can have a blast effect three to five times more powerful than HE equivalent.
WM-80火箭能配备多种弹头。它的HE弹头爆炸半径70米,而且一枚单一弹头能产生多达16800个碎片。反坦克聚簇弹头有380颗子弹头每颗能穿透80到100毫米的顶装甲。在试验中它是对抗装甲群和特别对抗装甲人员输送车非常有效的武器。可得的其它弹头包括燃烧弹和一种燃料-空气爆炸弹头,更强大超过HE当量的三到五倍。
WM-80火箭能配备多种弹头。它的HE弹头爆炸半径70米,而且一枚单一弹头能产生多达16800个碎片。反坦克聚簇弹头有380颗子弹头每颗能穿透80到100毫米的顶装甲。在试验中它是对抗装甲群和特别对抗装甲人员输送车非常有效的武器。可得的其它弹头包括燃烧弹和一种燃料-空气爆炸弹头,更强大超过HE当量的三到五倍。
The crew compartment of the launcher vehicle houses an advanced fire control unit. Aiming and firing process are fully automated. On receiving a firing order, data from GPS and C3I computers is feed into the fire control computer by the operator. The computer then calculates an optimal firing solution, also taking into consideration the weather, terrain conditions, and the ammo type used. The launcher then automatically elevated into firing position. It will fire the rockets in single shots or full automatic salvo mode depending on the selection made by the operator. A launcher vehicle crew consists of five crew members: a commanding officer, a driver, a mechanical engineer/gunner and two loaders. Usually all members of the crew help out with the reload.
发射装置车辆的组员舱有一个先进的火控单元。瞄准目标和发射程序被完全自动化。一收到一个发射命令,从全球定位系统和C3I(指挥、控制、通信和情报)计算机的数据被操作员的馈入火控计算机之内。计算机然后计算一个最佳发射方案,也考虑天气、地形条件和使用弹药类型的因素。发射装置然后自动升高进入发射位置之内。它将会发射火箭在单发或全自动齐射模式取决于操作员作出的选择。一套发射装置车辆组员由五名组员所组成:一名指挥官、一名驾驶员、一名机械技师/炮手和二名装载员。通常所有的组员在外面帮助再装填。
发射装置车辆的组员舱有一个先进的火控单元。瞄准目标和发射程序被完全自动化。一收到一个发射命令,从全球定位系统和C3I(指挥、控制、通信和情报)计算机的数据被操作员的馈入火控计算机之内。计算机然后计算一个最佳发射方案,也考虑天气、地形条件和使用弹药类型的因素。发射装置然后自动升高进入发射位置之内。它将会发射火箭在单发或全自动齐射模式取决于操作员作出的选择。一套发射装置车辆组员由五名组员所组成:一名指挥官、一名驾驶员、一名机械技师/炮手和二名装载员。通常所有的组员在外面帮助再装填。


The former Soviet republic of Armenia remain the only user of the WM-80 MRL.
前苏联亚美尼亚共和国一直是WM-80式MRL的唯一使用者。
According to Jane's Missile and Rocket, eight of such systems were sold to Armenia in 1999.
依照简氏导弹和火箭,八套这种系统在1999年被出售给亚美尼亚。
依照简氏导弹和火箭,八套这种系统在1999年被出售给亚美尼亚。
上一篇:没有了 下一篇:WEISHI SERIES MULTIPLE LAUNCH ROCKET SYSTEM
| WEISHI SERIES MULTIPLE LAUNCH ROCKET SYSTEM
中国“卫士”(WEISHI)系列多管发射火箭系统 |
| The WeiShi (WS) family of the multiple launch rocket systems were developed by Sichuan Aerospace Industry Corporation (SCAIC, also known as Base 062) in Chengdu, Sichuan Province.... [2017-08-12] |
| Brief History of PLA's Type 83 273mm Multiple Rocket Launcher System
中国83式273毫米多管火箭发射系统发展史 |
| In 1984, the plant finally rolled out the 273mm caliber MRL and designated as the Type 83 273mm MRL.... [2017-01-15] |
