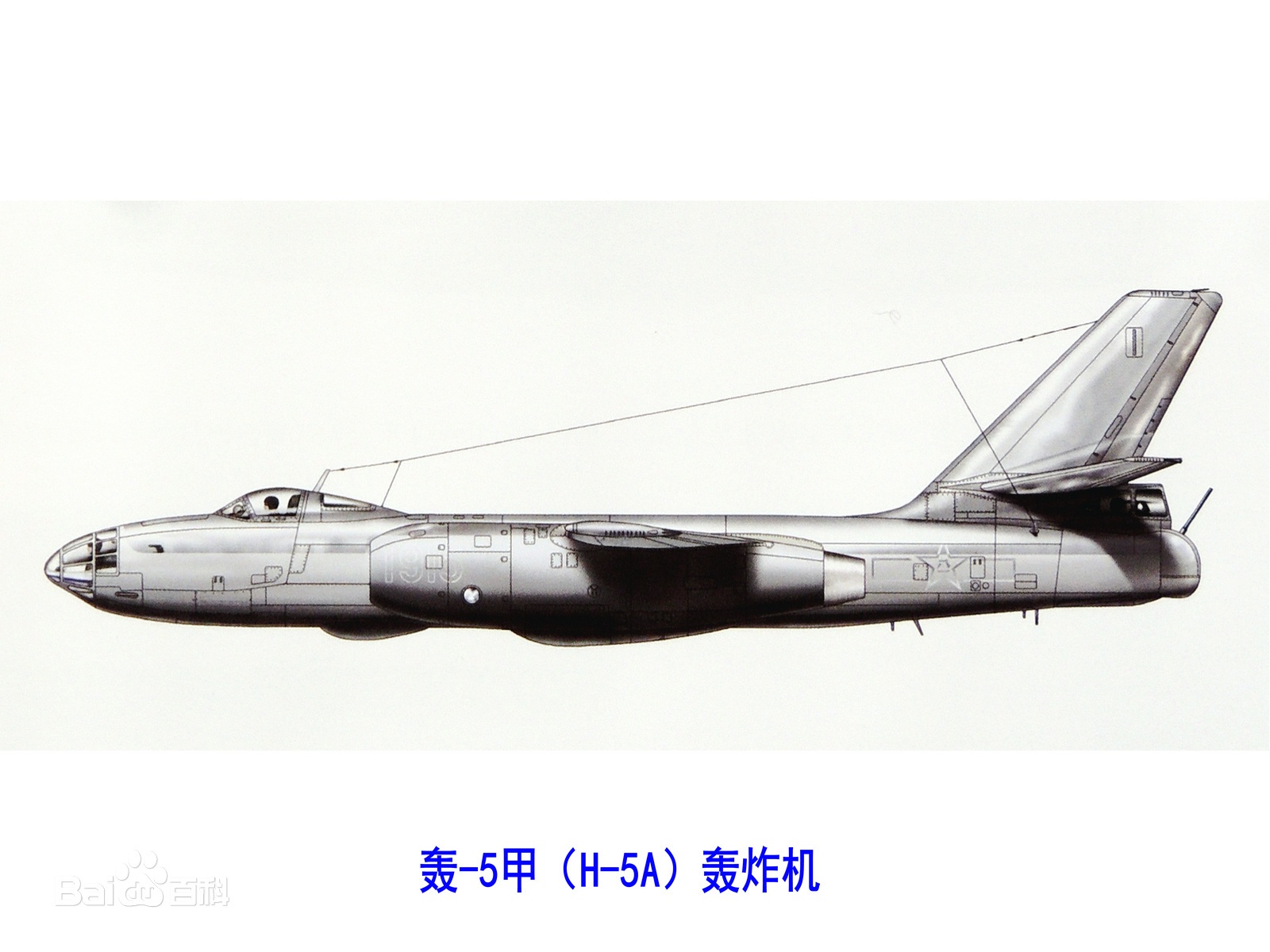
| H-5 Light Bomber[Il-28 BEAGLE (ILYUSHIN)]
中国H-5型[伊尔-28“猎兔犬”(ILYUSHIN)]轻型轰炸机 Date:2020-04-07 Source:wikia By:Globalmil Viewed: |

The reports of the demise of the H-5 seem somewhat exaggerated. It was asserted without citation in 1995 that the H-5 had been withdrawn from service, but the continued presence of the H-5 in the PLAAF inventory is widely attested by subsequent sources. The light bomber is a kind of tactical bomber and is used for close air support to the ground troop operations. Its bomb load is small but it is light, manoeuvrable and agile and has some peculiarities which make it irreplaceable by medium bombers. The Il 28 was the Soviet Union's standard light bomber, and was in use in all air forces of the Soviet Bloc. The 11-28 aircraft is a light bomber designed and produced in the Soviet Union. It flew for its first time in 1947 and entered into service in 1950. It was put into production in large quantities and was widely used in 1950s and 1960s because of its simple structure and low price.
关于轰-5(H-5)消失的报道似乎有些夸张。1995年有人断言轰-5已经退役,但随后的消息来源广泛证明了PLA清单中轰-5继续存在。轻型轰炸机是一种战术轰炸机,用于向地面部队提供近距离空中支援。它的炸弹负荷虽小,但重量轻,可操纵和敏捷,并且具有一些独特性,使其无法被中型轰炸机取代。伊尔-28型是苏联的标准轻型轰炸机,并已在苏联联盟的所有空军中使用。伊尔-28飞机是苏联设计和生产的轻型轰炸机。它于1947年首次飞行,并于1950年服役。由于其结构简单,价格低廉,已在1950年和1960年被大量使用。
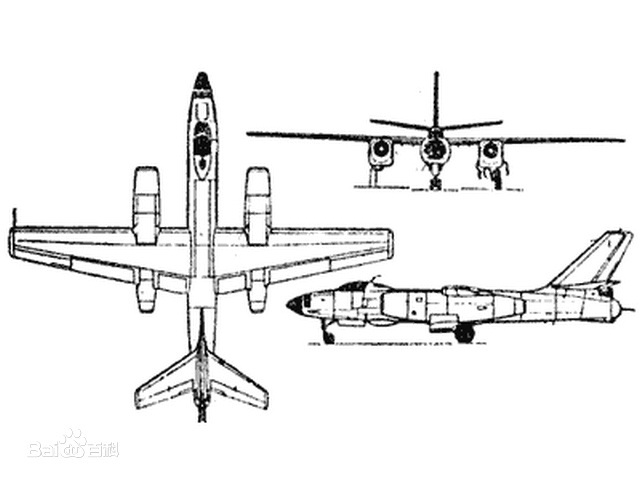
This aircraft was produced in China under the nomenclature H-5. The H-5 was a light subsonic bomber with a cantilever high set wing. The high-mounted wings have a straight leading edge and forward-tapered trailing edge with blunt tips. Two turbojets are mounted beneath the wings in pods. Pods extend beyond wings' leading and trailing edges. The fuselage is tubular and cigar-shaped tapering to the rear with a rounded, glassed-in nose and bubble canopy. The tail fin is swept-back and tapered with a blunt tip. Flats are low-mounted on the fin, swept-back, and tapered with blunt tips. A glassed-in tail gunner compartment is to the rear of the tail.
这种飞机在中国以轰-5的命名制造的。轰-5是轻型亚音速轰炸机,带有悬臂式上机翼。平直上单翼具有笔直的前缘和带有钝尖的前锥形后缘。在机翼下安装两台涡轮喷气发动机吊舱。吊舱超出机翼的前缘和后缘。机身为管状和雪茄形,向后逐渐变细,并带有圆形玻璃机鼻和气泡座舱罩。尾垂翼后掠,并带有钝尖的锥形。尾平翼低位安装在尾垂翼上,后掠,并带有钝尖的锥形。机尾后部有一个玻璃尾部炮手舱。
The prototype production of the H-5 was different from that of the H-6. It was not a complete licenced production, because a great number of design modifications were incorporated according to the military Services' operational requirements. The design modifications were made possible by the following: China imported a number of 11-28 bombers and a lot of suggestions were made by the military Services based on a long period of operation; the Harbin Aircraft Factory had repaired the I1-28s since the mid-1950s, manufactured main parts and components for the purpose of repairing and, therefore, mastered necessary manufacturing techniques, the factory was expanded and reconstructed on a large-scale for purpose of the H-6's prototype production and had capabilities for manufacturing production tooling, assembling a complete aircraft and then testing it in flight; and finally the factory had experienced prototype productions of the Z-5 helicopter and the H-6 medium bomber.
轰-5的原型生产不同于轰-6。它不是完整的许可仿制型号,因为根据军方的作战要求进行了大量的设计修改。通过以下方式进行设计修改:中国进口了11架到28架轰炸机,军方根据长期的操作提出了许多建议。 自1950年中期以来,哈尔滨飞机厂已经对伊尔-28飞机进行了维修,制造了主要部件进行维修,因此,掌握了必要的制造技术后,工厂就大规模扩建和改造,用于轰-6的原型生产,具备了制造生产工装,组装完整飞机然后在飞行中进行测试的能力; 最终,该工厂熟练的制造了直-5型直升机和H-6型中型轰炸机样机。
The Chinese built H-5 light bomber is an equivalent of the 11-28 aircraft but with some local improvement in design. Forty per cent of the original I1-28 design was modified. Main modifications were:
· A conventional structure wing was used to replace the wing which was spliced at the central line and, therefore, 110 kg of weight was saved.
· Major airborne equipment were in common with that of the H-6. One example was use of H-6's tail turret. Of course it introduced corresponding structure changes.
中国制造的轰-5轻型轰炸机相当于伊尔-28飞机,但在局部设计上有所改进。伊尔-28原始设计的40%被修改。主要修改为:
· 使用传统结构机翼代替了在中心线处拼接机翼,因此节省了110公斤的重量。
· 主要的机载设备与轰-6的设备相同。一个例子是使用H-6的尾炮塔。当然,它也带来相应的结构更改。
The operational performance was remarkably improved by use of a great number of new airborne equipment: a new radar with significantly increased operational range, a new sight which increased aiming angle and observation angle and hence bombing precision, the new turrent with an electrical control system which was good in the follow-up behavior, an increased ammunition capacity, higher rate of fire and longer effective firing range; and a new and improved friend-or-foe identification.
通过使用大量的新型机载设备,显着提高了操作性能:新的雷达具有更大的作战距离,新的瞄准具增加了瞄准角和观察角,从而提高了轰炸精度,新的炮塔配备了电控系统, 良好的跟踪性能,弹药容量增加,射速更高,有效射击距离更远;以及经过改进的全新“敌我识别”功能。
The Harbin Aircraft Factory initiated their preparation for the trial-production of the H-5 in 1963. They first corrected the drawings used for aircraft repair, and then supplemented with some drawings and data of stress analysis and aerodynamic computation and prepared a complete set of processing documents. The manufacturing of production tooling and aircraft parts began in 1964. Two prototype aircraft were completed in 1966 and one of them was used for static test. The static test was carried out from July to September and it proved that the structure strength was in conformity with the technical requirement. Another prototype flew for its first time on September 25, 1966. The H-5 aircraft was formally put into production in April, 1967.
哈尔滨飞机厂于1963年开始进行轰-5试生产准备工作。他们首先修正了用于飞机维修的图纸,然后补充了一些应力分析和空气动力计算的图纸和数据,并准备了一套完整的加工文件。生产工具和飞机零件的制造始于1964年。1966年完成了两架原型飞机制造,其中一架用于静态试验。7月至9月进行了静态试验,证明其结构强度符合技术要求。另一架原型机于1966年9月25日首飞。轰-5飞机于1967年4月正式投入制造。
Hu Xichuan, chief engineer, Qi Zhikun, vice chief engineer, Xiong Wenjie and Li Guangshu who were in charge of the design work, made active contributions to the development of the H-5. Sun Zhaoqing who was in charge of manufacturing techniques and his colleagues made bold innovations in managing manufacturing techniques. They applied some new techniques such as the plastic molds, combined fixtures and explosive forming, etc. so that the product quality was improved and the prototype production was completed in a shorter period of time. With support from various departments and agencies all over the country most of the necessary 3,200 materials and 334 vendor furnished equipment could be manufactured in China. The success in partial redesign of the H-5 marked the breaking away from the yoke of pure licenced production in area of bomber technology and the beginning of transition from modification and derivation to independent development.
负责设计工作的总工程师Hu Xichuan,,副总工程师Qi Zhikun,Xiong Wenjie和Li Guangshu为轰-5的发展做出了积极的贡献。负责制造技术的Sun Zhaoqing及其同事在管理制造技术方面进行了大胆的创新。他们应用了一些新技术,例如塑料模具,组合夹具和爆炸成型等,从而提高了产品质量,并在较短的时间内完成了原型生产。在全国各部门和机构的支持下,大多数必要的3200种材料和334种外方提供的设备都可以在中国生产。轰-5的部分重新设计成功标志着轰炸机技术领域摆脱了纯许可生产的束缚,也标志着从改型和衍生到独立开发的转变的开始。
Several derivatives were developed on the basis of the requirement of the military Services after the H-5 aircraft was certified and put into production. The PLA Air Force is equipped with several dozen of special-purpose electronic aircraft, including a few specially modified Hongdian-5 light bombers which have been equipped to support electronic warfare operations. However, the PLAAF remains some 15 years behind world standards in this field.
轰-5型飞机通过认证并投入生产后,根据军事需求开发了几种衍生型号。解放军空军配备了数十架专用电子战飞机,其中包括一些经过特殊改装的“轰电-5”轻型轰炸机,这些轰炸机已装备以支援电子战。但是,中国空军在这一领域仍落后世界标准约15年。
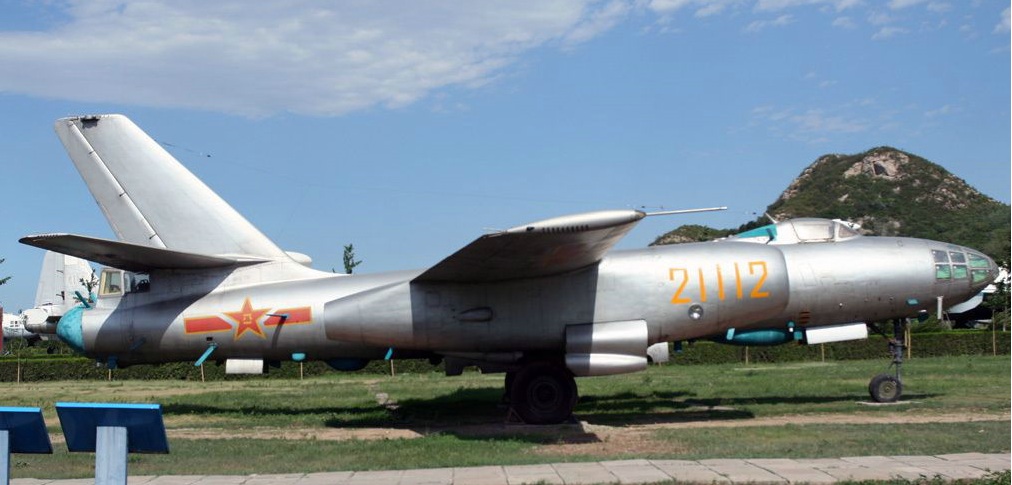

轰电-5电子干扰机
H-5 Nuclear Bomb Carrier
轰-5核弹运载机
In September 1967 the government assigned a task for retrofitting the H-5 into a nuclear carrier which could be used both for nuclear test and operational missions. A retrofitting group headed by Xia Zhenhua, assistant to chief engineer, and Sun Zhaoqing, chief technologist, was established in the Harbin Aircraft Factory. The task was satisfactorily fulfilled after their intense work in half a year and a H-5 nuclear carrier was successfully used in the nuclear test on December 27, 1968. Although a portion of China's jet light bomber force could be used in a limited strategic role, the H-5's low performance envelope mitigates against its use for strategic bombing.
1967年9月,政府下达了将轰-5改装为可用于核试验和作战任务的核运载机任务。哈尔滨飞机厂成立了以总工程师助理Xia Zhenhua和总技术师Sun Zhaoqing为首的改装小组。经过半年的艰苦努力,这项任务令人满意地完成了,一架轰-5核运载机在1968年12月27日成功地用于核试验。尽管中国的喷气轰炸机部队的一部分可以在有限的战略角色中使用 ,轰-5的性能低下使其无法用于战略轰炸。
HZ-5
轰侦-5
This was a photographic reconnaissance aircraft retrofitted from a H-5 prototype aircraft. Its design was started in December 1970 and was certificated in 1977. The main modifications were the addition of 2 large medium-high altitude day and night, aerial cameras inside the fuselage bomb bay and wing integral fuel tanks. Compared with the prototype aircraft its range was increased by 47 per cent, combat radius by 50 per cent and endurance by 1 hour and 23 minutes. The success of the HZ-5 filled a gap in the field of short / medium reconnaissance aircraft.
这是从轰-5原型机改装而来的照相侦察机。它的设计始于1970年12月,并于1977年获得认证。主要修改是机身炸弹舱内增加了2部大型中高空昼夜航拍相机和机翼一体式燃油箱。与原型飞机相比,其航程增加了47%,战斗半径增加了50%,续航时间增加了1小时23分钟。轰侦-5的成功填补了中小型侦察机领域的空白。
HJ-5
轰教-5
The Harbin Aircraft Factory began to develop the bomber-trainer HJ-5 in the mid-1960s to satisfy the need in training military Services' bomber pilots. The new off the shelf vendor-furnished-equipment and components were selected by the factory. But in order to improve air crew's environment, the air condition system was redesigned to properly heat or cool the cockpit. The HJ-5 prototype production began in May 1967, its first flight took place on December 12, 1970 and its design certification was awarded by the government in April 1972. A total of 186 HJ-5s were produced. The success of the HJ-5 development closed a gap in the area of the bomber-trainer and ended the history in which the training of bomber pilots depended upon imported foreign trainers.
哈尔滨飞机厂从1960年代中期开始研发轰炸机-教练机轰教-5,以满足军队训练轰炸机飞行员的需要。工厂选择了新供应商提供现成的设备和组件。但是为了改善机组人员的环境,对空调系统进行了重新设计,以适当加热或冷却驾驶座舱。轰教-5原型机的制造始于1967年5月,其第一次飞行于1970年12月12日进行,其设计认证于1972年4月获得政府颁发。总共生产了186架轰教-5。轰教-5研制成功填补了轰炸机-教练机领域的空白,并结束了轰炸机飞行员的培训依赖引进外国教练员的历史。

HJ-5
轰教-5
补充内容:《轰-5》来源:百度百科
1、轰-5轰炸机于1963年1月开始研制,1966年9月25日首架轰-5在哈尔滨试飞成功。1967年4月,轰-5轰炸机通过国家鉴定,投入批量生产,随后装备中国空军部队。该机于1984年停产,总共生产545架。轰-5已经于2009年5月全部退出中国空军现役战机序列。
2、除基本轰炸机外,轰5 还有鱼雷轰炸机、核弹投放机、HJ-5(轰教5)教练机和 HZ-5(轰侦5)、HD-5(轰电5)侦察、电子对抗机等机型。
3、轰-5采用了两台涡喷-5甲型涡喷发动机,该发动机是歼-5使用的涡喷-5的改型。涡喷-5甲发动机是沈阳航空发动机厂(黎明机械厂)试制的,1957年9月8日涡喷-5甲发动机(轰-5轻型轰炸机的动力装置)经国家鉴定验收,转入成批生产。涡喷-5甲发动机,单台推力26.48千牛(2700千克)。
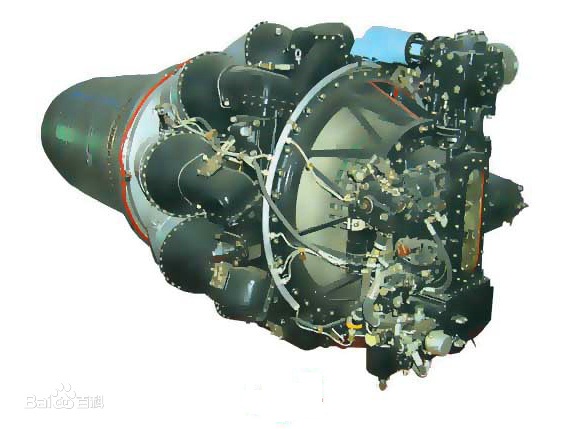
涡喷-5甲型涡喷发动机
4、轰-5轰炸机上主要航空电子设备设备包括轰炸雷达、自动领航仪、敌我识别器及各种通讯导航器材等。轰-5机组包括3名乘员,领航员舱在机头,驾驶员在其身后气泡形驾驶舱内,机尾有与前方不连通的通信射击员舱。
炸弹舱在机身中部,正常载弹量1000千克,最大载弹量3000千克。机头设有一门固定航炮,机尾炮塔有两门活动航炮。炸弹舱内携带4枚500千克或12枚250千克炸弹。翼下还有8个挂架,可挂火箭弹或炸弹。机头机尾各装两门23mm机炮,总备弹量为650发。
5、轰-5甲(H-5A),轰-5甲,是中国航空工业哈尔滨飞机制造厂于1967年9月根据国家下达的任务改装的一种核武器运载机。保密代号为2152。
6、轰-5鱼雷型,1965年,海军航空兵提出在轰-5飞机上改装挂鱼雷的要求,1966年开始改型设计。主要改进项目:可在机外挂3枚鱼雷或2枚大型鱼雷和2组弹舱内副油箱。
1969年11月30日,轰-5鱼雷型由王文英首飞成功。到1980年为止,共交付海军35架。为部队改装伊尔-28飞机100多架,部队反映良好。
7、轰-5雷达试验机,网络上曾经出现过轰-5改装的歼轰-7雷达试验机照片。歼轰-7装备的JL-10A“神鹰”脉冲多普勒雷达,首先在轰-5试验机上试飞试验。中国试飞院的这张照片,显示了轰-5轰炸机头部,改装了歼轰-7的机头和雷达。这反应了中国在军机研制中,因地制宜、小步快跑的务实策略,利用和挖掘老旧机型的潜力,投资少、研制风险低,为新型机研发打下坚实的技术基础和经验储备。
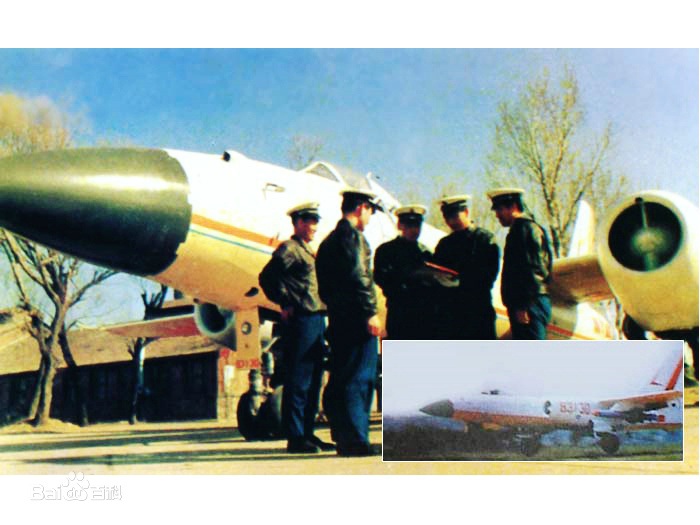

轰-5雷达试验机
8、轰电-5(HD-5),轰电-5很少见于官方的报道。中国空军的轰电-5能执行软压制对方防空系统的能力。原来轰电-5准备加装YJ-5反辐射导弹,由于改型研制导弹下马未成,而YJ-91导弹则体型弹重过大,轰-5挂载较为吃力,实际使用效果不明。更多的用途是类似美国的EA-6B一样,从事电子对抗/干扰任务。
轰-5轰炸机参考数据
乘员 3人
长度 16.77米
翼展 21.45米
高度 6.20米
机翼面积 60.8平方米
主轮距 7.4米
前主轮距 6.67米
空重 12890千克
最大起飞重量 21200千克
动力系统 两台WP-5甲型涡喷发动机,单台推力26.48千牛(2700公斤)
载油量 3800千克
载弹量 3000千克
最大飞行速度 902千米/小时
实用升限 12500米
航程 2400千米
作战半径 560千米
翼载荷 348.7千克/平方米
推重比 0.25
起飞滑跑距离 980米
着陆滑跑距离 930米
武器 炸弹舱在机身中部,头部一门固定航炮,尾部两门活动航炮
上一篇:H-6 MEDIUM BOMBER 下一篇:没有了
| H-5 Light Bomber[Il-28 BEAGLE (ILYUSHIN)]
中国H-5型[伊尔-28“猎兔犬”(ILYUSHIN)]轻型轰炸机 |
| This aircraft was produced in China under the nomenclature H-5. The H-5 was a light subsonic bomber with a cantilever high set wing.... [2020-04-07] |
| H-6 MEDIUM BOMBER
中国空军H-6中型轰炸机 |
| The Hong-6 (H-6, or B-6 in its export form) is a Chinese copy of the Russian Tupolev Tu-16 (NATO codename: Badger) twin-engine, medium-range bomber. It is the PLA’s principal medium- to long-range air strike platform. ... [2017-02-18] |

